Non Conventional sources of energy are available in abundance as they regenerate naturally after every use.
We can continuously harness renewable energy sources like Solar, Wind, and HydroPower, etc. through a sustainable approach as they can replicate themselves in nature.
Non conventional energy sources are clean, inexpensive, and pollution-free, unlike conventional sources such as petroleum.
Owing to the unlimited usage of conventional energy sources, they are likely to be exhausted someday as they take a much more extended period to develop.
Thus, to reduce our dependency on fossil fuels, we need to switch over to renewable energy sources.
In this article, we will discuss:-
- What are the various forms of alternate energy sources available in India?
- Importance and uses of non-conventional sources of energy.
- Future of non conventional sources of energy.
[lwptoc titleFontSize=”130%” itemsFontSize=”120%” backgroundColor=”#ffffff” borderColor=”#60d60c”]
Non Conventional Sources of Energy in India
Here are the top 8 Important Non conventional sources of energy in India and their importance;
1. Solar Energy
Do you know which is the most widespread and abundant non-conventional source of energy in India?
Yes, It is solar energy that has the greatest potential among all the available nonconventional energy sources.
Being a tropical country, India receives abundant sunshine and has a vast potential to generate electricity from solar energy.
Most Indian Regions have 300 – 330 sunny days in a year and receive around 4-7 kWh per sq. m per day of sunshine that is equivalent to over 5000 trillion kWh/year of energy.
In 2017-18, energy consumption in the form of electricity stood at 11,30,244 GWh (refer to the graph below), which is well below the equivalent solar energy received.
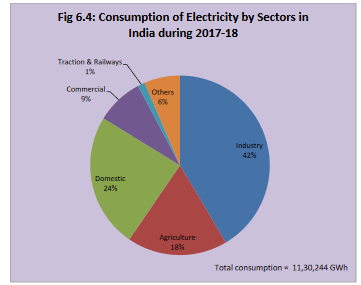
Do you know that solar energy availability on earth for 45 minutes is enough to meet our energy demand for one year?
Amazed!
Yes, that is true theoretically, but it requires a suitable technique to convert solar energy into other energy forms.
The major problem with this non conventional source of energy is that the sunlight is widespread and is challenging to store and utilize.
However, with upcoming advanced technologies, India managed to utilize solar energy on a large scale and acquired the 5th global position in solar power deployment.
As per the Ministry of New & Renewable energy, India, Solar power capacity had increased by more than 11 times in the last five years from 2.6 GW in March 2014 to 30 GW in July 2019.
Now a piece of good news for you!
A recent study reveals that India’s current solar tariffs are 20-30 percent below the cost of existing thermal power and up to half the price of new coal-fired power.
National Solar Mission (NSM), a significant initiative by the Indian government to promote sustainable growth, targets the installation of 100 GW grid-connected solar power plants by the year 2022.
Uses of Solar as Non Conventional Source of Energy

We can harness solar power for domestic, commercial, or industrial purposes and use it in two ways:
- Use direct Solar heat to boil water or dry food grains
- Use Photovoltaic cell (PV) cells that directly convert sunlight into electricity.
Several gadgets based on solar power are available in the market and are used extensively in rural India.
Some of them are :
- Solar Cooker
- Water heater
- Dryer
- Lantern
- Pumps
- Lighting
2. Wind Energy

It is a clean and inexhaustible energy source for generating power by capturing the wind’s kinetic energy.
India has a diverse climate, and certain regions are quite windy.
For wind power generation, it goes like the windier, the better.
The Power generated by a wind turbine is proportional to the cube of the wind speed.
It means that if the average wind speed increases from 6 to 7 m/s, it will result in 60% more power from the same turbine.
Thus, for optimal power generation, it is vital to install wind turbines that are exposed to strong wind currents.
There are some limitations for setting up windmills, as they require locations where the wind velocity is at least 6.5 m/s.
The technology for harnessing wind energy has become commercial in some developed countries, but it is still in the preliminary stage in India.
According to the Indian Meteorological Department, an average annual wind velocity of 6.5-8 m/s is available at several places in peninsular India, along the coastlines of Gujarat, the Western Ghats, and some parts of central India.
A report from CSE states that:-
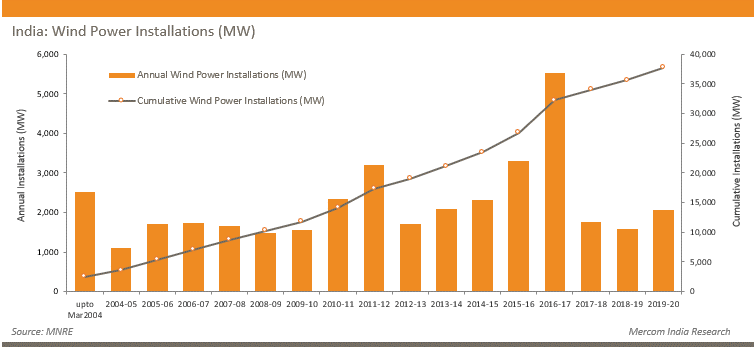
India currently has the fourth-highest wind installed capacity globally with a total installed capacity of 37.7 GW (as of March 2020) and has generated around 52.66 Billion Units during 2017-18.
A recent study by Crisil states that wind installations may reach 45 GW by March 2022.
What are the Various uses of Wind energy?
The following are some of the uses of this non conventional energy source:-
1. A standard windmill produces approx. Fifty-five kilowatts of electricity daily can be used locally or attached to the electric grid for powering homes and businesses.
2. Windmills prevent earthquakes where continuous wind flow causes soil erosion.
3. Wind pumps utilize Wind energy for pumping water. India’s government has installed several wind pumps with a pumping capacity of 20 – 400 liters at many locations.
4. Wind energy reduces the environmental impact of electricity generation, as it requires no fuel and does not cause air pollution.
3. Biogas

Biogas is typically a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and nitrogen in various proportions prepared by the fermentation of organic material.
Methane and carbon dioxide percentage decide the calorific value of the fuel.
At 40 % methane content, the calorific value is 3200 kcal/cubic meter, while at 50 %, it increases to 4500 kcal/cubic meter.
Being an indigenous source and environmentally clean technology, biogas offers a robust solution to the present energy crisis in rural India.
A report by the Institute for Social and Economic Change states that around 95 percent of the livestock population is available in rural areas that can harness 48,220 million cubic meters of biogas per year.
Indian government planned to install around 5,000 Compressed Bio Gas (CBG) plants across the country by 2023 using the following feedstock.
- Agriculture residues
- Cattle dung
- Spent wash of distilleries
- Sewage water
- Municipal solid waste
- Biodegradable fractions of industrial waste.
- Sawdust
India’s immense agricultural potential provides enormous quantities of agro-residues that can be used to extract energy from biomass.
Uses of Biogas as a Non Conventional Energy Source
In developing countries like India, biogas is an excellent and effective way to promote rural development.
Following are some of the uses of biogas:-
- Cooking, Heating, Lighting & Power Generation
- Biogas slurries can produce organic manure that can be a good substitute for chemical fertilizers for agriculture.
- Sanitation problems can be solved as toilets are directly linked with biogas plants.
4. Tidal Energy

Tidal energy is a type of non conventional energy produced by ocean movement during the rise and fall of currents.
Energy from the tides can be predicted more accurately than wind or sun due to the massive size of oceans.
The rise and fall of ocean water occur twice in a lunar day (as high & low tides) thus tidal energy is continuously available and predictable.
Alternating water currents generate a high amount of power as compared to air even at low velocity, as water is denser than air.
These moving currents contain enormous kinetic energy that one can harness for power production.
Tidal waves also contain potential energy at a point when water is at a higher elevation than normal.
A tidal stream turbine is a device that is used to convert the kinetic energy of the moving water into electrical energy.
Tidal Power plants can only be installed across the coastlines as they receive 02 high & low tides in a day.
A study conducted by the Indian Government in 2014 stated that India has a tidal power potential of 12.5 gigawatts spread across the coastlines of Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, and West Bengal.
But due to high costs associated with the installation of tidal power plants this plan is postponed till further notice.
However, globally, many European countries increased their tidal power generation capacity from 5 gigawatt-hours in 2009 to 45 gigawatt-hours in 2019.
What are the Various Uses of Tidal Energy?
There are limited applications of tidal energy and some of them are:-
- Power generation
- Grains Crushing
- Water Purification
5. Geothermal Energy

The core of the earth contains a vast source of thermal energy that is still untapped.
Geothermal energy is a form of renewable energy derived from the enormous heat continuously produced and stored inside the earth.
Natural hot water springs, fountains, hot dry rocks, and volcanic magma mainly contain this inexhaustible non-conventional energy resource.
Early civilizations were using geothermal energy in the form of hot springs for different purposes like bathing and washing.
In India, natural hot springs at many places such as Badrinath & Gangotri in Uttarakhand and Rajgir in Bihar are perceived as a ‘gift from god.’
Currently, Italy, the USA, New Zealand, Japan, Mexico, the Philippines, Indonesia are some countries that use geothermal energy for electricity generation and other thermal applications.
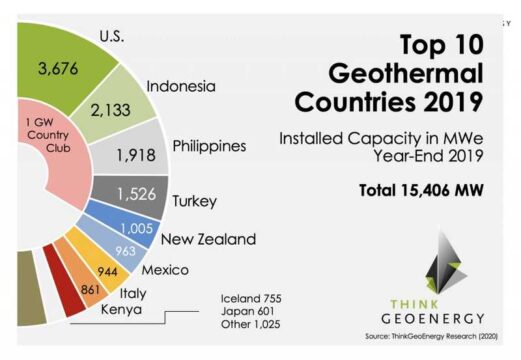
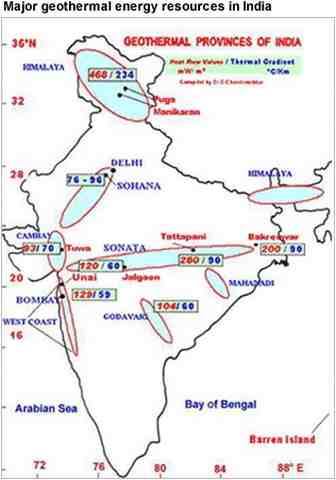
Geological Survey of India (GSI) conducted various studies and identified 350 geothermal energy locations in the country, having an estimated potential of about 10,000 MW.
Below you can some of the important sites that are explored in India.
By now, most countries have started to recognize the immense potential of geothermal energy that can meet the growing energy demand.
With advanced technologies, it is possible to generate power from this non-conventional energy resource in India.
Uses of Geothermal as Non-Conventional Energy Source?
Geothermal energy has multiple uses and some of them are:-
- Surface reservoirs fulfill many domestic applications such as heating, cooking, bathing, and washing
- Geothermal heat pumps for commercial heating purposes
- Power generation
- Greenhouse Cultivation
- Salt Extraction
6. Hydropower
Hydropower is the energy produced from water that utilizes its kinetic energy to produce electricity.
Free-flowing water (from stored reservoirs & dams) spins a turbine that creates electricity similar to wind energy.
India has the largest hydropower reserves that are capable of meeting the demand of around 85 GW.
A report by the International Hydropower Association states that India has a total installed capacity of 50 Gigawatt in 2020 and overtaken Japan to become the fifth-largest hydropower producer in the world.
The northern and northeastern regions of India have colossal Hydropower potential.
Arunachal Pradesh has the highest untapped hydropower potential of 47 GW, followed by Uttarakhand with 12 GW.
In India, certain remote and hilly areas are difficult to electrify, and power transmission is costly.
Small hydropower (SHP) plants having a station capacity of up to 25 megawatts (MW) prove helpful for these locations as they run on small turbines and do not require building a dam on a river.
The Indian government is primarily focusing on SHP as compared to large hydropower plants as the former is more environmentally friendly.
Small hydropower plants can further be classified into micro hydro (up to 100 kW), mini-hydro (101–2000 kW), and by Jun 2020 total of 4688 MW of power is produced by SHP.
However, hydropower plants are getting less traction nowadays as solar plants are becoming cheaper day by day.
What are the Various Applications of Hydropower?

Some of the important uses of Hydropower are:-
- Electricity production
- Flood & draught Control
- Irrigation
- Environmental services
- Recreational Activities
7. Energy from Gasohol
Gasohol is a mixture of Gasoline (up to 90%) and Ethanol (up to 10%) when used as a fuel.
Ethanol, also known as Ethyl alcohol or simply alcohol is made from barley, corn, sugarcane, or similar crops by a fermentation process.
In order to reduce toxic gas emissions, the use of ethyl alcohol as an alternative fuel has increased in many parts of the world including India.
Ethanol when successfully blended with petrol (gasoline), increases the octane rating of fuel and due to low carbon emissions, it is less harmful to the environment.
According to India’s National Biofuel Policy 2018, an ethanol blending target of 10% by 2022 and 20% by 2030 has been set but until 2019 mere 5% of the blending target is achieved.
The government of India has recently announced in 2021 that the earlier 20% ethanol blending target in petrol ( E20) is revised to 2025 from 2030.
What are the Various Applications of Gasohol?
Gasohol is mainly used as fuel in Gasoline Engines.
8. Hydrogen Energy
Hydrogen energy is one of the cleanest, as it does not create any carbon-based emissions.
The technology of Hydrogen production from fossil fuels is in use today.
However, hydrogen fuel cell technology is still in its nascent stage in India.
In fuel cell technology, the electrolysis of water (H2O) produces hydrogen when electricity passes between the electrodes immersed in a conducting aqueous solution.
Hydrogen fuel cells are modular in design and relatively easy to transport.
Like regular Batteries, they share the same electrochemical foundations, applying electrolyte and membrane materials.
The energy density of Hydrogen fuel is higher as compared to other fuels; thus, it produces more energy.
Currently, Hydrogen is made from fossil fuels which are responsible for environmental degradation.
Thus, the Indian government should prioritize hydrogen manufacturing from renewable sources only.
India’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has been supporting various hydrogen projects in academic institutions, research organizations, and industry for development.
In 2019, Tata Motors, in collaboration with the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) and Indian Oil (IOCL) launched a hydrogen fuel cell bus.
Hyundai also seeking to launch its first fuel cell NEXO SUV in India by 2021, and plan to build the required hydrogen infrastructure to support the vehicles near Delhi.
Indian government must come up with a cost-effective plan to develop fuel cell technology on a commercial scale, as it is still costly.
Applications of Hydrogen as Non Conventional Energy Source
Some of the essential uses of Hydrogen energy are:-
- Electricity Production
- Transportation
- Industrial applications
- Residential applications
- Commercial applications (providing back-up power for telecom towers)
Conclusion
India has vast reserves of non conventional sources of energy that are still untapped.
Unlimited use of fossil fuels, increasing imports, demand-supply gaps, and environmental concerns are some of the key drivers for renewable energy.
Currently, India is relying heavily on coal energy, hydropower, and fossil fuels for electricity production.
However, India has vast sources of renewables such as solar, wind, biomass, and small hydro whose potential exceeds the present installed generation capacity.
That is indeed a significant figure, and we see this sector has a great future ahead.
What do you think about the future of non-conventional sources of energy in India?
Please provide your comments below and share this article to help others.
To join the Save Environment bandwagon consider subscribing bharatgogreen.
References:-
- Pal, Kunwar & Yadav, P. & Tyagi, S.. (2017). Renewable Sources in India and Their Applications. 10.1007/978-3-319-50219-9_3.
- Kumar, Ashwani & Kumar, Kapil & Kaushik, Naresh & Sharma, Satyawati & Mishra, Saroj. (2010). Renewable energy in India: Current status and future potentials. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 14. 2434-2442. 10.1016/j.rser.2010.04.003.
- Ministry of New & Renewable Energy
- TERI: Innovative Solutions for Sustainable Development
- https://vikaspedia.in
- Overview of Renewable Energy Potential of India by Peter Meisen, Global Energy Network Institute (GENI)