Global warming refers to an increase in the average temperature of the earth’s atmosphere due to the emission of various greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrous oxide, and methane.
It has emerged as one of the most significant environmental issues arising from our day-to-day activities.
Global warming can change the earth’s climate and alter the heat and radiation balance.
Over the years, atmospheric carbon dioxide levels amplified from 320 ppm (1960) to 416 ppm (2021) that resulted in a steady temperature rise.
In India, global warming has led to increased precipitation, droughts, and melting of glaciers, causing floods, hurricanes, and storms.
Uttarakhand glacier burst leading to an avalanche and flash flood in Chamoli district on February 7, 2021, is a perfect example of climate change.
In this essay, we will provide all information about global warming and discuss:
- What is Global warming?
- Cause & effect in points
- Ideas for prevention of global warming at the personal level.
[lwptoc titleFontSize=”130%” itemsFontSize=”120%” backgroundColor=”#ffffff” borderColor=”#5fd60a”]
What is Global Warming [Defintion]?

Global warming results from a steady rise in temperature near the Earth’s surface in the last one or two centuries.
Climate scientists have gathered extensive measurements of various weather patterns (such as precipitation, temperatures, & storms) or associated effects on climate (such as ocean currents and the atmosphere’s chemical composition) since the mid-twentieth century.
Different findings show that Earth’s atmosphere has shifted in nearly any possible timescale after the dawn of geologic time.
Since the Industrial Revolution, various human activities altered the existing greenhouse and resulted in radical climate change.
The combustion of fossil fuels such as coal and oil has raised carbon dioxide accumulation in the atmosphere over the past century (CO2).
The clearance of land for agriculture, manufacturing, and other human activities has also raised greenhouse gas emissions to a smaller degree (Matawal & Maton, 2013).
Global warming and Climate Change
We are using both the terms interchangeably, but NASA states that global warming is long-term warming of the planet.
In contrast, climate change is a broader set of changes happening on Earth.
Global warming is limited to temperature rise, whereas climate change refers to
- Rising sea levels
- Shrinking mountain glaciers,
- Abrupt wind patterns
- Accelerating ice melts
- Shifts in flower/plant blooming times.
I hope now you understood the difference between global warming and climate change.
Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect | How Earth become Warm?
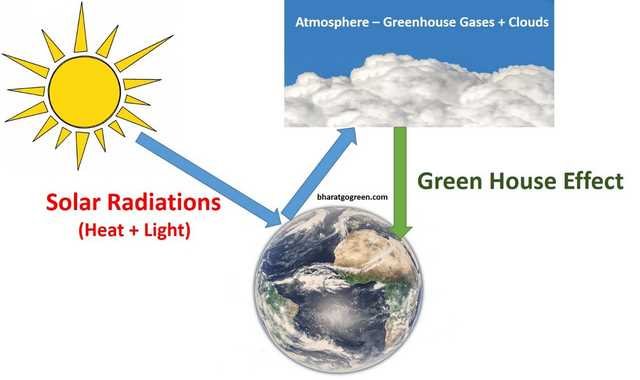
We know that global warming refers to an increase in the average earth’s temperature due to the natural greenhouse effect caused by greenhouse gases.
Do you know how the earth becomes warm?
Let us take an example!
Imagine you left your car in a parking lot on a bright sunny day.
The heat and light from the sun would eventually get trapped inside your car, and it becomes hotter.
This is similar to the greenhouse effect, where the sun’s heat and light are trapped in the earth’s atmosphere, causing temperature rise.
You may ask how the gases are trapped?
Our earth has a natural greenhouse system that radiates the trapped heat back to the surface when no sunlight is available.
This is required to maintain the temperature and keep our planet warm even at nighttime.
Various human activities such as fossil fuel burning and deforestation resulted in an increased amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Extra CO2 in the atmosphere amplifies the greenhouse effect causing the earth to become warmer than it would be naturally.
Global Warming Causes and Effects
| Causes | Effects |
| Deforestation | Rise in Temperature |
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Extreme Weather |
| CFC Release | Sea Level Rise |
| Industrial Revolution | Ecosystem Threats |
| Agriculture | Climate Change |
| Increasing Population | Disease Spread |
| Volcanoes | Increased Mortality Rates |
| Water Vapors | Reduction in Natural Habitat |
| Melting Glaciers | Adverse effect on species |
| Forest Fire | Adverse effect on coral reefs |
Global Warming Causes
There are multiple causes of global warming, and we can further divide them into human-made and natural causes.
Let us see one by one.
Man-made Causes of Global Warming
1. Deforestation

Plants are the primary source of oxygen for us.
They consume carbon dioxide and release oxygen, enabling the atmosphere to retain its balance.
Cutting and burning forests for residential & industrial purposes have contributed to an imbalance in the climate that has resulted in global warming.
A data by globalforestwatch indicates that the total area of humid primary forest in India decreased by 3.2% from 2002 to 2019.
Thus, it is very important to protect our trees and forests to breathe and live.
2. Emission of Green House Gases

This is the major cause of global warming due to the continuous emission of carbon dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, methane, etc., into the atmosphere.
Do you have any idea who is responsible for maximum CO2 generation?
Yes, they are the power plants that are responsible for more than 40% of CO2 release in the world.
The burning of fossil fuels (coal, diesel, and natural gas) for electricity generation is responsible for GHG emissions.
Excessive use of fertilizers and nitric acid plants are the main sources of nitrous oxides.
Vehicle use, except for a short distance, produces a variety of exhaust pollutants.
Vehicles consume fossil fuels, which release a lot of carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the environment, causing a temperature rise.
3. Release of Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC)

Humans have been releasing CFCs into the environment due to their heavy use of air conditioning units and refrigerators, which has a detrimental effect on the atmosphere’s ozone layer.
The ozone layer shields the earth’s atmosphere from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays.
The use of CFCs has resulted in ozone layer destruction, allowing ultraviolet rays to enter the atmosphere, raising global temperature.
4. Industrial Revolution
The earth’s temperature has been rapidly growing since the start of industrialization.
The toxic pollution from factories contributes to the planet’s rising temperature.
The Intergovernmental Commission on Climate Change confirmed in 2013 that the temperature increase by 0.9 degrees Celsius between 1880 and 2012.
As contrasted to the pre-industrial average temperature, the rise is 1.1 degrees Celsius.
5. Agriculture
Several agricultural operations generate carbon dioxide, nitrous oxides as well as methane gas.
Due to this fact, the amount of greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere rises, increasing global temperatures.
6. Increase in Population

Check out the graph above that shows population growth in billion units and CO2 levels in millions of metric tons.
It looks like population growth and climate change are directly related, and an additional person increase causes carbon emissions to go up.
When the population increases, so do the number of people breathing.
As a result, the atmosphere’s carbon dioxide volume increases, which is the main global warming source.
Natural Causes of Global Warming

1. Volcanoes
Volcanoes are one of the most critical natural factors related to global warming.
Volcanic eruptions release ash and smoke into the atmosphere, changing the climate.
2. Water Vapors
Water vapor is a form of greenhouse gas.
If the earth’s temperature rises, more water evaporates from water sources and remains in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.
3. Melting Glaciers
Wherever there are glaciers, there is permafrost.
It’s a frozen ground that’s been trapped in greenhouse gases for years.
Gases are emitted back into the atmosphere when permafrost melts, increasing global temperatures
4. Forest Fires
Wildfires, also known as forest blazes, create a significant volume of carbon-containing pollution.
These gases are released into the atmosphere, inducing global warming by raising the temperature of the earth.
Global Warming Effects / Consequences
Following are the consequences of global warming;
1. Rise in Temperature

Because of global warming, the earth’s temperature has increased sharply.
Consequently, the sea level rise due to the melting of ice.
Coastal areas can suffer disastrous effects as a result of this.
Rising temperatures intensify air pollution by raising ground-level ozone.
The key ingredient of smog is ground-level ozone, and the colder it gets, the more of it we get.
Asthmatics who breathe dirty air are more likely to be taken to hospitals and suffer.
It deteriorates the health of people who have heart or lung disease.
Warmer temperatures also increase the amount of pollen in the air, which would be bad news for people who suffer from seasonal and other allergies.
2. Sudden Extreme in Weather Events
Another result of global warming is extreme weather.
Despite several of the hottest summers on record in the United States, much of the world has endured colder-than-normal winters.
Climate change will allow the polar jet stream, which separates the cold North Pole air from the warm equatorial air, to move south, taking cold Arctic air.
3. Sea Level Rise

Water levels increase as the ice melts in particular.
The global sea level is rising at a rate of 0.12 inches every year on average, according to the World Meteorological Organization in 2014.
This is almost twice the 20th century’s average annual growth of 0.07 inches.
There is a prediction that sea levels may rise rapidly when polar ice melts in the Arctic, Antarctic, America, Europe, Alaska, South America, and Asia.
4. Ecosystem Threats
Global warming can influence coral reefs, resulting in the disappearance of plants and animals.
Rising global temperatures have exacerbated the fragility of coral reefs.
5. Impact on Climate Change
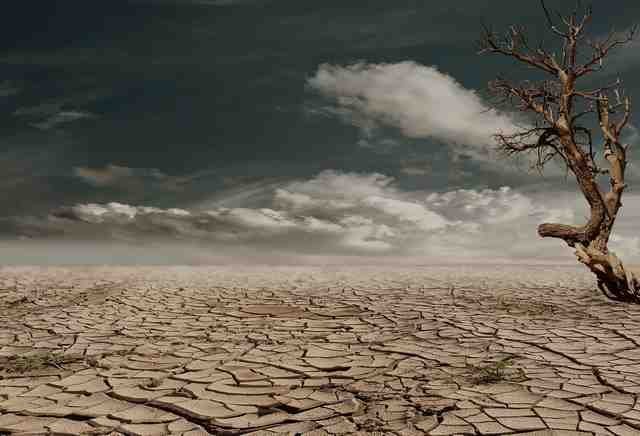

Global warming can cause abrupt climatic changes.
Some areas are experiencing droughts, while others are experiencing flooding.
In India, around 40 million hectares of land are prone to floods where sudden floods can occur at any time.
The most vulnerable states of India are Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Assam, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Punjab West Bengal, Gujarat, Orissa, Andhra Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir.
Similarly, 68% of the total agricultural land in India is prone to droughts, of which 33% is chronically drought-prone, receiving rainfall of less than 750mm per year.
Maharashtra, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Orissa are most susceptible to draughts.
Global warming can cause a drastic shift in the season’s cycle too, where summers are getting longer than winter months.
6. Spreading of Regional Diseases
Because of global warming, water vapors and heat levels have changed dramatically.
This has resulted in the proliferation of disease-carrying mosquitos.
Warmer temperature helps bacteria and microbes to grow at a faster rate that can induce some new diseases.
7. Increase in Mortality Rates
The annual death toll typically rises as flooding, tsunamis, and other natural disasters become more frequent.
Furthermore, such activities have the potential to transmit illnesses that endanger human life.
8. Reduction in Natural Habitat
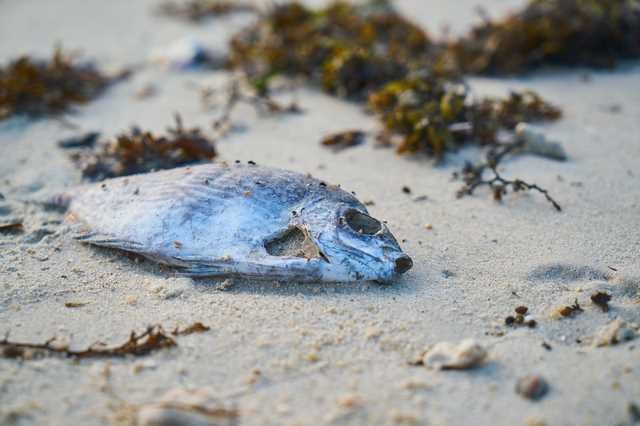

Several animals and plants lose their ecosystem because of global climate change.
In this situation, the species are forced to abandon their natural environment, and all of them become extinct as a result.
Another big effect of global warming is on wildlife.
9. Effects on Species
Climate change places one of every six species at risk of extinction.
Plants, animals, and birds facing climate change have two choices for survival: transfer or adapt.
With the current climate change rate, it is always impossible for a species to evolve rapidly enough to keep up with its shifting surroundings.
Travelling is becoming more difficult because of habitat loss.
10. Effects on Coral Reefs
Rising temperatures or acidity in our oceans is intensifying extreme coral bleaching incidents, such as the one that killed more than a third of the Great Barrier Reef in 2016.
How to Reduce / Stop Global Warming [Solutions]
Various nations, including India, have taken major steps to stop global warming.
Kyoto agreement is a collaborative effort that has been made between various nations and nonprofit organizations to reduce the emissions of various greenhouse gases.
We can even make many efforts at a personal level to combat climate change.
Here are some of them;
1. Education
We cannot fully prevent global warming but can minimize its impact.
So how can we do this?
We can do it simply by self-learning and educating others about the cause and effect of global warming.
Many blogs like us create awareness about such burning environmental issues.
You can visit them, read and educate others.
2. Use Renewable Energy Sources
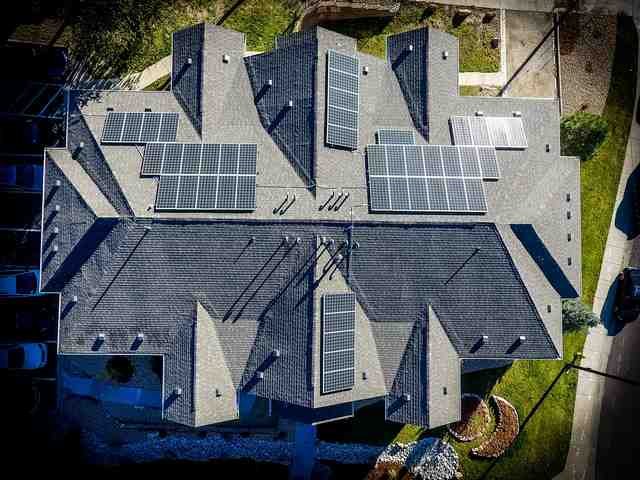

The Indian government is promoting Green energy technologies such as solar & wind and providing various incentives to consumers who are interested in installing them.
This initiative will help to curb air pollution in the long run.
Choose a utility that derives at least half of its electricity from renewable energy sources.
If it is not an option, check the electric bill; several utilities now list additional opportunities to promote clean energy on their financial statements and websites.
3. Use of Energy-Efficient Appliances

Since 1987, reliability requirements for thousands of appliances and devices have prevented 2.3 billion tons of carbon from entering the atmosphere.
That’s almost the same volume of CO2 produced worldwide by about 440 million cars.
When shopping, look for the Energy Star logo on washing machines, fridges, and other appliances.
4. Reduction of Wastewater
Conserving water also helps to minimize greenhouse emissions.
It’s because pumping, heating, and treating the water uses a lot of electricity.
So take shorter baths, switch off the faucet while brushing your teeth, and replace your fixtures and appliances with Water Sense-labeled models.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency, refurbishing two out of every 150 People’s households with water-effective plants can conserve nearly 150 billion KW-hours of electricity per year, avoiding 85,000 tons of CO2.
5. Eat Local
Approximately 10% of the United States’ energy is used to produce, manufacture, box, and ship food, with around 40% of it winding up in landfills.
Therefore, it is important to use local products without packaging.
6. Use of LED Bulbs
LED bulbs are almost 75% more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent fluorescent (CFL) bulbs. They are even more cost-effective in the long run:
In India, the price of LED bulbs reduced from 400 rupees in 2014 to about 50 rupees in 2020.
Gram Ujala Yojna scheme now offers the world’s cheapest LED bulbs in rural India at a throwaway price of 10 Rupees.
According to Energy Efficiency Services (EESL), an average Indian family can save around Rs. 4,000 per year on their power bills by shifting towards LED bulbs.
7. Use Fuel-efficient Vehicles

Gas-efficient cars, like hybrids, including completely electric vehicles, save both money and gas.
Switching towards renewable fuels can reduce toxic emissions at fuel stations in the long run.
8. Use Public Transportation & Shared Vehicles.
Conventional vehicles are the major contributors to air pollution.
By using shared vehicles (such as carpooling) or public transportation and encouraging others to use them will definitely reduce global warming.
It will also save money and energy.
Conclusion
Carbon emissions and global warming are here to stay for a while.
To minimize its effect, try to educate as many people around you about the repercussions of global warming.
The Indian government is doing many things like formulating “The clean air act” and promoting electric vehicles to curb global warming.
To reduce the consequences of global warming and climate change, we must change our energy usage patterns in favor of less carbon-intensive energy generation, transportation, and forest and land use management.
What are your views about this essay on global warming?
Please provide your comments below and share this article to help others.
To join the Save Environment bandwagon consider subscribing bharatgogreen.
References
- Global warming – Causes of global warming. (2021). Retrieved 20 March 2021, from https://www.britannica.com/science/global-warming/Causes-of-global-warming
- Global Warming 101. (2021). Retrieved 20 March 2021, from https://www.nrdc.org/stories/global-warming-101
- Matawal, D., & Maton, D. (2013). Climate Change and Global Warming: Signs, Impact, and Solutions. International Journal Of Environmental Science And Development, 62-66. doi: 10.7763/ijesd.2013.v4.305
- What Is Global Warming?. (2021). Retrieved 20 March 2021, from https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/article/global-warming-overview
