Are you aware that air pollution has become a severe threat to India because out of the ten most polluted cities in the world, nine are located here?
Yes, you heard it right; a 2018 report by World Health Organization on the most polluted places on earth says so.
These cities are Kanpur, Faridabad, Varanasi, Gaya, Patna, Delhi, Lucknow, Agra & Muzaffarpur, where PM (Particulate Matter) 2.5 average varies from 120 – 173 μg/m3.
This value is much higher than WHO’s recommended value of 10 μg/m3 (max).
Here, PM2.5 is the smallest particle, which can enter the lungs and cause serious health problems.
Isn’t this data alarming?
What do you think?
In this air pollution essay, you will get a clear idea about the following:-
- What are the causes of air pollution?
- What are its effects?
- How to control air pollution in India?
This descriptive essay is helpful for school as well as college-level students.
What is Air Pollution?

Our environment can dissipate various hazardous gases, dust, or smoke, which are released into the atmosphere.
When the release rate exceeds the normal capacity of the environment, then the concentration of harmful components will increase, causing air pollution.
In a broad sense, air pollution means :
- Contaminating the air (indoor or outdoor) with certain harmful components such as gases, dust particles, or fumes.
- These components are usually not present in the air and can lower their quality, causing harm to living beings.
What are Air Pollutants?
We know that pollution means the introduction of harmful components into the environment.
Pollutants are harmful components, which are responsible for air pollution.
They can be natural like volcanic ash or can be man-made like dangerous gases from various industries.
Some examples are Oxides of Sulphur & Nitrogen, carbon monoxides, VOCs, dust particles, or fumes.
Particle pollution can be most dangerous and affects people more than any other type of pollution, even in lower concentrations causing an increased mortality rate.
| Further Reading! |
What are the different types of Air Pollutants in India?
Air Pollutants can be classified into solid particles, liquid droplets, or gases.
These pollutants can be further classified into the following categories.
1. Primarily Air Pollutants
Primary air pollutants are emitted ‘directly’ from a source or process such as volcanic eruptions or sulfur dioxide emissions from factories.
The major primary pollutants are Oxides of Sulphur & Nitrogen, Methane, Ammonia, Chlorofluorocarbons, Toxic metals, BTX, etc.
2. Secondary Air Pollutants
Secondary air pollutants cannot be emitted directly instead they are formed by the reaction of primary pollutants with themselves or with other components present in the environment.
The most important secondary air Pollutants are:
- Ground Level Ozone– Formed when hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides (NOx) combine in the presence of sunlight
- Smog– created by the interactions of several primary pollutants
- Acid rain– Formed when oxides of sulfur or nitrogen react with water.

In India, Ozone is under the list of regulated pollutants but its monitoring is extremely limited.
Only a few state pollution control boards in megacities of Delhi, Kolkata, Bengaluru, etc. have initiated ozone monitoring but they are not coming under any program.
3. Particulate Air Pollutants
They may come under primary pollutants but they are discussed here separately as particulate matter is the most dangerous among all.
Particulate air pollutants or particulate matter (PM) is a microscopic solid or liquid matter suspended in the earth’s atmosphere.
Broadly particulate air pollutants come under:-
Coarse particles: Particles that lie between 10μm to 2.5μm
Fine particles: Particles having a diameter less than 2.5μm
There are various subtypes of particulate matter:
- PM10 : Particle size less than 10 μm in diameter
- PM2.5 : Particles size less than 2.5 μm in diameter
- PM1.0 : Particle size less than 1 μm in diameter
A report from the health effect institute (see graphic below) states that the population in most Indian states (21) and minor territories (6) are exposed to PM2.5 levels above the Indian annual standard of 40 μg/m3 as recommended by the National Ambient Air Quality Standards of India.
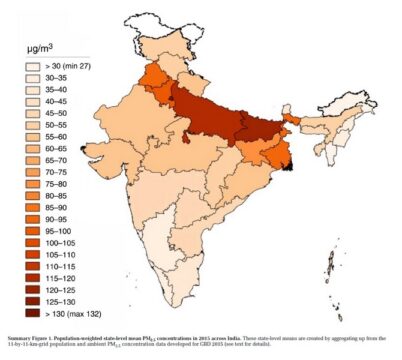
In their report, they mentioned that If no action is taken PM2.5 exposures are likely to increase by more than 40% by 2050.
What are the Various Causes of Air Pollution in India?
The following are the major causes of air pollution in India:
1. Burning of crop residue after the harvesting season
Crop residue burning is the topmost source of the air pollution problem in India.
According to WHO’s data, Delhi and the NCR region have the worst air quality and crop burning is a major contributor to that.

Post harvesting, north Indian farmers usually burn the crop (Wheat and Rice) residues so that they could prepare the field for seeding in the next season.
Agricultural waste burning releases a large amount of unburnt fine carbon particles (due to incomplete combustion) into the atmosphere causing air pollution.
2. Indoor burning of Biomass as a fuel
In most parts of rural India, conventional solid fuels such as dung cakes, wood, sawdust, dried plants, and charcoal are still burned for general cooking needs.
These are burned in open, makeshift, less efficient cooking stoves that cause permanent haze & smoke in the environment.
Burning solid biomass emits a variety of chemical substances in the form of gases and particulate matter.
In addition to small particles, biomass burning produces toxic pollutants such as carbon monoxide, oxides of nitrogen, formaldehyde, benzene, poly-aromatic hydrocarbons due to incomplete combustion, which adversely affects an individual’s health.
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW), Government of India had developed a national exposure model (2013) for solid fuel using household-level estimates average PM2.5 exposures and found these shocking results:
| Average Exposure
(Daily basis), μg/m3, |
Reference Limit
Indian Standards, μg/m3 |
|
| Men | 204 | 40 |
| Women | 337 | 40 |
| Children | 285 | 40 |
3. Toxic Emissions from Factories cause Air Pollution
Industrial toxic emissions are key sources of air contamination.
Various industries are causing air pollution by burning fuels, carrying out chemical processes, and releasing particulate matter into the environment.
Refineries, Petrochemicals, waste incinerators, power plants, food processing, packaging, manufacturing, metals & mining industries emit high levels of greenhouse gases, hydrocarbons, particulate matter, and chemicals into the air, thus depleting the air quality.
Indian energy sector such as power plants is predominantly coal dominated and India is the second-largest consumer after China.
Most of the Coal-fired power plants are inefficient and emits oxide of carbon/nitrogen/sulfur, fluorinated gases, arsenic, lead, mercury, and other metals in bulk amount, which leads to air contamination.
4. Agricultural activities
Agricultural activities in India involve heavy usage of Nitrogenous fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides & insecticides, which contain highly toxic Volatile organic compounds (VOC).
The application of fertilizers causes ammonia emissions, which are responsible for deteriorating air quality.
5. Vehicular Emissions Cause Air Pollution
Today, transportation has become a vital part of our daily life and we are unable to live without it.
A recent study done by TERI in the NCR region reveals that 28 % of PM2.5 emissions were caused by vehicles in which heavy commercial vehicles (Buses, Trucks, etc.) pollutes the most (9%).
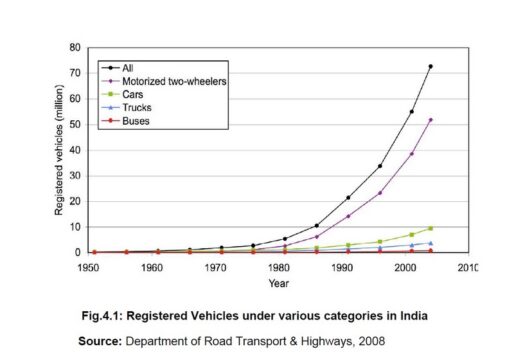
Due to the internal combustion of fuel, vehicular exhausts contain dangerous gases such as carbon monoxide, oxides of nitrogen & sulfur, hydrocarbons (PAH), and particulates.
Vehicular emissions cause an enormous amount of pollution, which is very difficult to manage nowadays.
In addition to the above, traffic congestion in India is equally responsible for polluting the air.
Due to traffic congestion, the average speed of the vehicle is reduced so, in turn, fuel is burned inefficiently, thus more pollution occurs per trip.
| Further Reading! |
6. Construction and Demolition Activities
A recent report by the World Health Organization ranked Mumbai as the fourth most polluted megacity of the world, and 63rd among 400 most polluted cities of the world.
Due to rising construction and infrastructure activities across the city, more and more pollutants are being trapped in the air.
According to NEERI- National Environmental Engineering and Research Institute – “Construction activity accounts for about 30% of dust particles, followed by vehicular emissions.
In the construction sector, brick kilns are equally contributing to air pollution.

Apart from construction activities, the demolition of older buildings may contain a series of banned chemicals stated below that may pose a special threat to the people.
- Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) used in electrical components
- Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) used in building materials
- asbestos, etc.
Any construction site has poor air quality due to fine airborne contaminants and volatile compounds, which can spread to the surrounding area due to wind.
The main construction contaminants that spread around by wind include
- PM10 (particulate matter with a diameter less than 10 microns generating polluted dust)
- PAHs bound to particulate matter
- VOCs (volatile organic compounds)
- Asbestos
- Gases such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxides.
7. Indoor Air Pollution

Due to any activity, if smoke, chemicals, or foreign particles are contaminating indoor air (contained within our home, office, or classrooms, etc.) then it is called Indoor Air Pollution.
Some of these activities are:
a. Smoking
It releases a series of toxic chemicals, some of which are carcinogenic in nature.
b. Household Products Storage & Use
Household cleaning products, sprays, paints, varnishes, etc. contain certain organic toxic chemicals, which are highly volatile.
Due to their volatile nature, we can sense their smell in the air and these are predominantly responsible for indoor air pollution.
Paints, varnishes, cleaning, disinfecting, cosmetic, and degreasing products contain organic solvents.
c. Dry cleaning
This process emits small amounts of chlorinated solvents (such as PCE – perchloroethylene) or petroleum solvents into the atmosphere.
When dry-cleaned clothes are kept in an enclosed space (such as a wardrobe), it could pose a health risk and cause air pollution.
d. Building Materials and Furnishings
Asbestos-containing insulation, damp carpet, furniture made of certain pressed wood products, central heating, and cooling systems (HVAC) are the major contributors to indoor air pollution.
e. Building Heating contributes to Air Pollution
Usage of gas heaters, wood stoves, fireplaces, etc. room heating releases major pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and particulate matter into the atmosphere causing air pollution.
8. Incineration of waste & Landfill disposal
Depending on the waste composition, incineration generates various toxic gases and particulate matter.
Natural decaying activity in the landfill disposal area generates methane which can be considered as a major greenhouse gas, an asphyxiant, and highly flammable.
This is dangerous to the environment if landfills are not well monitored.
9. Electronic waste
The majority of electronic waste (e-waste) from developed countries is being exported illegally to developing countries especially China, India, and Pakistan.

This is due to the lower labor costs and lack of governmental regulations.
In India, a large no of people is involved in unscientific dismantling, chemical leaching of printed circuit boards, burning of wires, burning of electrical & electronic components which generates a huge amount of toxic gases & VOCs.
These are detrimental to human health and the environment.
10. Natural Causes of Air Pollution
a. Wind
Air currents can move pollutants from the ground and transport them over large areas affecting people.
b. Dust & Wildfires
A report by the forest survey of India (2016-17) states that actual forest cover in India is 21% of the total area of the country.
In recent years forest fires in India have been increased.
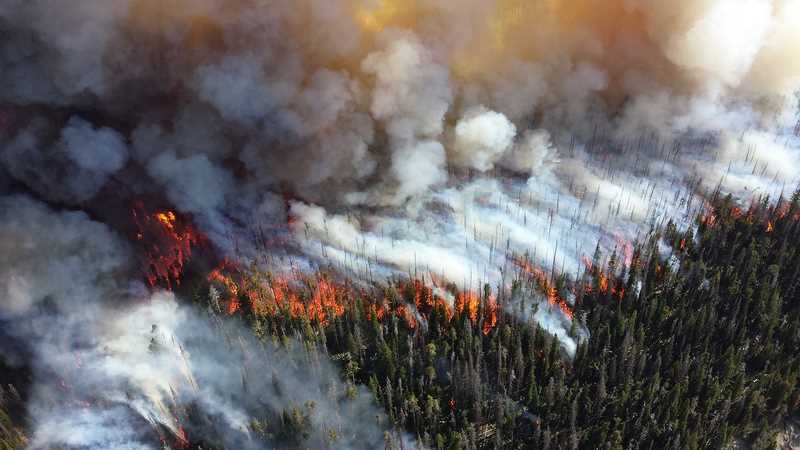

Forest fires cause air pollution by releasing particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and organic contaminants such as PAHs into the air.
c. Deforestation
India has witnessed rapid deforestation in recent years, primarily due to its focus on economic development.
Recent government data suggest that approx 14,000sq km of forests were cleaned to build 23,716 industrial projects across India over the last 30 years
Deforestation affects the atmosphere in many ways that lead to air pollution.
Forests act as a sink for carbon dioxide and this process called carbon sequestration.
Deforestation reverses the effects of carbon sequestration and releases greenhouse gases (including carbon dioxide stored in trees) into the atmosphere.
Data suggests that 25% of the world’s total greenhouse gas production comes from deforestation alone.
d. Microbial decaying processes
This activity cause air pollution due to the natural release of gases (especially methane) into the atmosphere
What are the Effects of Air Pollution?
Air Pollution Health Effects
Air pollution can cause harm when the concentration of pollutants is high in the air.
The majority of Indian People live in areas where urban smog, particle pollution, and toxic pollutants pose serious health concerns.
Air pollution can severely affect the Respiratory, Cardiovascular & Nervous systems due to ambient and household exposure to PM2·5.
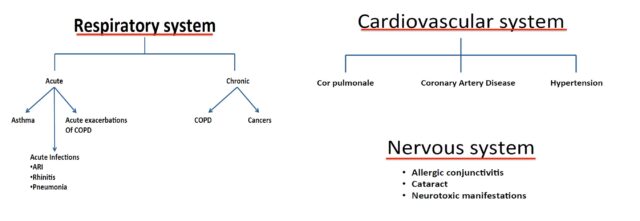
Who is at most risk?
Air pollution is a problem for all of us. However, the overall risk is dependent upon the individual immunity status.
Some persons are particularly sensitive to common air pollutants such as particulates and ground-level ozone.
Children, old-aged people, pregnant women, and persons with heart or lung diseases are prone to health hazards.
Air Pollution Environmental Effects
Air pollution not only affects human health but can cause a variety of environmental impacts too.
Some of the effects are:
1. Global warming
In simple terms, global warming is the incremental rise of the average temperature on Earth due to various greenhouse gases (such as Co2, methane, and Fluorinated gases, such as hydrofluorocarbons).
Global warming can affect human health, agriculture, water resources, forests, and wildlife.
A recent study done by IIT Delhi scientists shows that greenhouse gases released by various human activities are mainly responsible for the warm climate in India.
They compiled 50 years past data and found that in five decades average temperature in India rose approx. 0.5 degree C
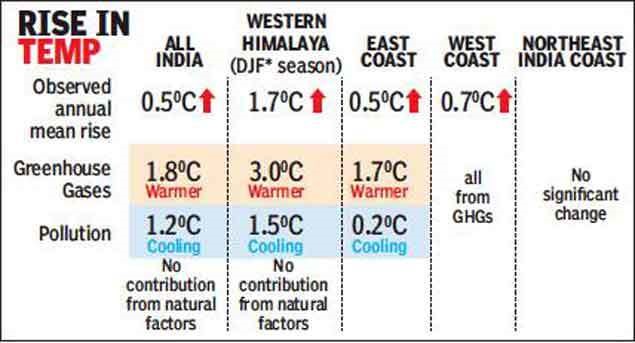
2. Acid rain
Acid rain is a sort of precipitation that contains a high amount of nitric and sulfuric acid.
These acids are formed primarily by oxides of nitrogen and sulfur which are released into the atmosphere
The burning of fossil fuels releases harmful gases like oxides of nitrogen and sulfur into the atmosphere.
During rain, water droplets combine with these air pollutants and become acidic. Then they fall on the earth in the form of wet precipitation (rain, snow, or fog) or dry precipitation (gas and particulates).
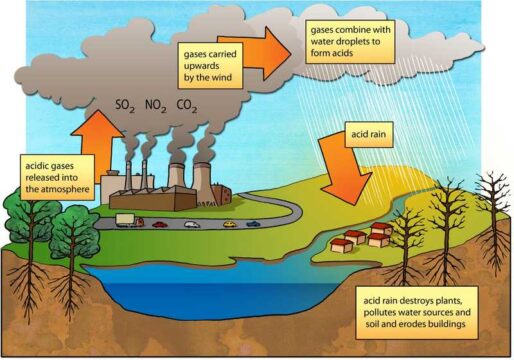
Normal rain is slightly acidic in nature having a pH of 5.6, while acid rain generally has a pH between 4.2 and 4.4.
Acid rain can cause damage to humans, wildlife, crops, water bodies, and forests.
IIT Mumbai has conducted some studies on acid Rain by compiling the last three decades of data.
They found that the pH values are higher (pH>7.0) in the north & northwest parts of India and slightly lower (6.0 ≤ pH ≤7.0) in the northeastern & southern parts of India.
3. Eutrophication
Eutrophication is a condition developed on the water surface when a high concentration of nitrogen (present in some pollutants) stimulates the growth of algae.
These algal blooms (green colored) can block the sunlight from getting into the water and harm the plants and aquatic animals that need it.
Although it is a natural process, various human activities also accelerate eutrophication.
A recent study on the Yamuna River in Delhi states that approximately 15% of people contribute phosphorus-containing wastewater effluents to rivers and lakes, causing eutrophication.
Other sources include the use of fertilizers, faulty septic systems, and erosion into the lake.

Nitrogen oxide emission from vehicles, power plants & chemical factories is equally responsible for nitrogen entering into the aquatic ecosystems.
4. Smog & Haze
Smog is a mixture of smoke and fog in the air.
This is formed due to various air pollutants such as oxides of nitrogen, dust particles, and water vapor.
These pollutants interact with sunlight to form ground-level ozone, which leads to haze formation.
This can reduce visibility and cause frequent breathing problems.
Power plants, industrial facilities, vehicles, crop burning, and construction activities are the major contributor to Haze & Smog.
Delhi is already facing this problem for the last few years.
5. Ozone layer depletion
Ozone in gaseous form is present at Earth’s upper atmosphere (stratosphere) as well as at ground level.
Stratosphere ozone is termed as ‘good’ ozone’ as it forms a blanket that protects human life from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays.
Ground-level ozone is called ‘bad’ ozone as it is a pollutant and affects human health.
In India, Ozone-depleting substances such as chlorofluorocarbons & hydrochlorofluorocarbons are widely used in refrigerants, polymers, pharmaceuticals, and agricultural chemicals.
Due to the prolonged thinning of the ozone layer, an increased amount of UV radiation can reach the earth’s surface and cause skin cancer and eye problems.
They can also damage the wheat & rice crops.
How to Control Air Pollution?
Control Measures by the Indian Government to Reduce Air Pollution

Air pollution control requires action in multiple sectors and the Indian government has launched several initiatives in the past to overcome this issue.
In 2011, CPCB has released a detailed report on air quality monitoring and its implementation.
Some of the initiatives are –
1. Ministry of Environment has set various emission standards for the brick manufacturing industry and imposed guidelines to manage agricultural residues so as to reduce stubble burning.
2. Ministry of Power has set specific guidelines to reduce the particulate matter emitted by coal-fired power plants and other energy-intensive industries.
3. Direct shifting from BS-IV to BS-VI emission standards and vehicle up-gradation to more fuel-efficient standards
4. Public transport availability enhancement by the Ministry of Urban Development.
5. Mechanisms to reduce air pollution will be included in the Smart Cities Mission launched by the Government of India.
6. In order to reduce dependency on solid fuel and tackling indoor air pollution, the Prime Minister of India launched the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana scheme back in 2016.
7. National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) was launched in early 2019 to control air pollution across the country. A national target is set that will reduce harmful particulate matter concentration by 20 to 30 percent until 2024.
8. India generates about two-thirds of the electricity from coal, but India has pledged in the Paris Climate Agreement to generate 40% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030.
9. Indian government implements the usage of CNG and LNG as an alternative fuel until the development of efficient and affordable electric vehicles. Oil Ministry is preparing a road map to open more CNG stations in the country.
10. Building Materials and Technology Promotion Council proposed to make use of fly ash bricks mandatory for all construction agencies.
11. The Indian government has drafted an auto fuel vision 2025 policy to minimize the contribution of vehicular usage to curb urban air pollution in the shortest possible period.
12. The Indian government is promoting electric vehicles by providing various incentives & tax benefits. With the launch of the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020 and schemes like FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric), the electric vehicle industry will definitely get a boost.
How to Reduce Air Pollution [10 Actionable Suggestions]

Although the Indian government is formulating various laws to regulate air pollution, there are a number of things that each individual may do to limit air pollution
The following are a few suggestions to make pollution-free India:
Vehicles are the major contributors to air pollution so using shared vehicles (such as carpooling) or public transportation and encouraging other people to use them will definitely reduce air pollution.
It will also save money and energy.
2. Raise Public Awareness about Air Pollution
The majority of people are unaware of this global issue and unknowingly they become a part of it.
We need to educate people (especially the village side) and our children to raise awareness about air pollution.
From time to time media should publish and spread information about air pollution.
3. Conserve Energy & use Energy-Efficient Devices
Energy conservation means less power demand, which in turn reduces air pollution.
Everyone should consider the star energy ratings while buying any electric appliances.
We must switch off all electric appliances when we are not using them.
Everybody must use LED lights as they live longer and consume less electricity compared to conventional ones.
They will help you to cut down the electricity bills and reduce pollution by consuming less energy.
4. Use Green Energy to Reduce Air Pollution
The Indian government is promoting Green energy technologies such as solar & wind and providing various incentives to consumers who are interested in installing them.
This initiative will help to curb air pollution in the long run.
We must use smokeless stoves to minimize CO2 emissions and reduce indoor air pollution.
We have to move slowly towards electric vehicles which are the transport of the future.
5. Plant a Tree – Reduce Air Pollution
Make earth cleaner and greener by planting more & more trees.
Inculcate this habit in your children so that they can also contribute to this noble cause and make pollution-free India.
By planting trees, we can reduce the effect of global warming and air pollution to the minimum possible extent.
6. Reduce, Reuse and Recycle
We have to concentrate on reuse and recycle products to lower energy usage.
We must use recyclable packaging and paper bags in our daily life.
It is better to use the paper from both sides for printing and photocopy purposes.
Do not simply throw away the items that are of no use, instead reuse them for some other purpose (for example, use old jars for storing cereals)
7. Use Natural Cleaning Products in Daily Life
Household cleaning products are volatile and contain toxic chemicals that cause indoor air pollution.
Use only water-based products that contain a low content of volatile organic compounds (VOC) to prevent indoor air pollution.
Use airtight containers for storing paint or solvents, which can prevent leaks and spillage.
8. Open your Windows Daily
Believe it or not but opening your house windows daily for a mere 15 minutes can make a huge difference in indoor pollution levels.
Daily open your windows for proper ventilation after painting, cleaning, or cooking.
9. Do not Burn Garbage in an Open Environment
Open burning of garbage is a common activity in India that aggravates air pollution.
Everyone must keep the garbage at designated locations or should dump it in waste bins provided by the municipality.
10. Proper Inspection & maintenance of vehicles and following PUC Norms
By doing regular inspection & maintenance, you are reducing 30-40% of air pollution load from your vehicle.
Obtain PUC certification for your vehicle on a regular basis.
Essay Conclusion…
In this air pollution essay, we learned about the cause, effect, and control of air pollution.
Air is a vital requirement for all living beings on this earth.
However, today, we have polluted this air so severely that it is becoming a threat to our lives.
Air pollution in India has increased rapidly, and the Indian government has taken various initiatives to control air pollution.
Now it is our turn to protect our mother nature and make India pollution-free.
Please comment and tell us about your contribution in reducing air pollution.
Also, let us know what you think about this descriptive essay on air pollution.
To join the Save Environment bandwagon consider subscribing bharatgogreen.
Please share this article to help others.
References:
- World Health Organization (https://www.who.int/health-topics/air-pollution)
- Air Pollution in Delhi (http://cpcbenvis.nic.in/envis_newsletter/Air%20pollution%20in%20Delhi.pdf)
- Air Quality Standards (https://cpcb.nic.in/)
- Air Pollution from Thermal Power Plants in India (https://www.cprindia.org/)
- TERI Report – Source Apportionment of PM2.5 & PM10 concentrations of Delhi NCR for identification of major sources