Do you know that Ecosystem maintains the natural balance on earth?
You may say –
“That’s OK, but what is an eco-system and why do we need it on this planet?”
Most of us think that it is associated with animals only, but actually, it consists of plants and non-living things too.
Really!
Yes, It is.
Just turn the pages of your biology textbook and try to recollect some old concepts.
In simple terms:
| An ecosystem consists of living & non-living community and their physical environment interacting with each other as a system. |
Life is not possible on this planet without them and that is why it is very important for us.
So, come & join this discussion to refresh our concept and get knowledge about:
- What is meant by an ecosystem?
- Classification of ecosystem
- Their Importance in our daily life
Ecosystem: Meaning & Definition
Let us take an example to get a better understanding of what does ecosystem means.
Lions and deers are a part of an ecosystem in which these two creatures are interrelated to each other.
How?
The prime reason is ‘survival’ where lions eat deer to survive.
This is a well-known relationship and each relation like this has a knock-on effect on other organisms, plants, and the environment of the same area.
Now let us imagine that the number of lions is less than deer then what will happen.
The deer community starts to flourish like anything, which in turn consumes more plants and vegetation causing their scarcity.
Thus, you can see how plants came into the picture in the above-cited example.
| Ecosystems are interrelated and any imbalance in them can cause several problems. |
I hope you have understood the concept of the ecosystem.
Now, let us define it like this (Ecosystem Definition)
- The interrelationship between living community (such as plants, animals & other organisms) and their non-living environment (such as air, sun, water, soil & atmosphere).
- It tells us how all these diverse communities live in close proximity and interact with each other.
Each community/organism in the ecosystem has its role to play and any external factor can cause a significant threat by deforming the natural balance of the ecosystem.
There are many external factors that you can think of, ranging from natural (such as tsunami) to man-made (such as air pollution) that can damage the ecosystem.
What are the Components of an Ecosystem?
There are two main components of an ecosystem:
1. Biotic (Living Components) |
Biotic components are different forms of life, such as plants, animals, and microorganisms.
They are further divided as :
-
Producers or Autotrophic components
Green plants that prepare their own food.
-
Consumers or Heterotrophic components
Animals and all Non-green plants which take food from autotrophs
-
Decomposers
They are fungi and bacteria that degrade and convert the dead residues of producers & consumers into simpler compounds to make them suitable for reuse by producers or green plants.
2. Abiotic (Non-living Components) |
Abiotic components of an ecosystem consist of nonliving, inorganic, and organic elements that help biotic components to survive.
Biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem are always interacting and affecting each other.
Abiotic components of an ecosystem are:
- Climatic factors like temperature, sunlight, humidity, precipitation.
- Gases, wind, water, soil
- Carbon, phosphorus, nitrogen
| More to Read! |
What are the Types / Classification of Ecosystem?
The classification of an ecosystem also known as ‘Biomes’ can be broadly done in two ways:
- Terrestrial
- Aquatic
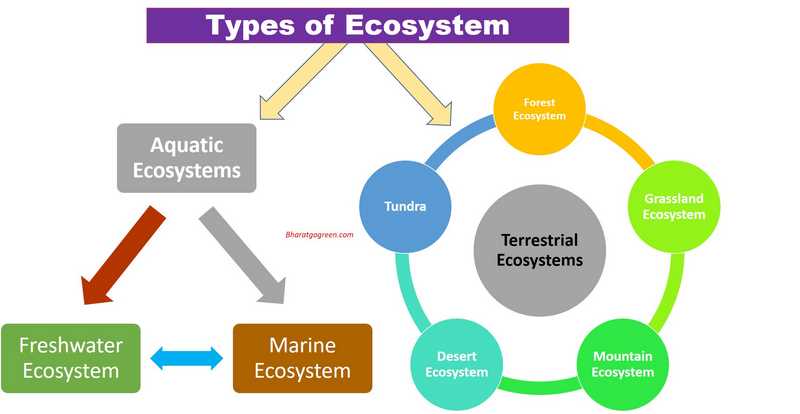
1. Terrestrial
|
This type of ecosystem is land-based in which different communities of animals, plants, and organisms are residing.
There are many types of terrestrial ecosystem on this planet but the most common ones are:
i. Forest Ecosystems
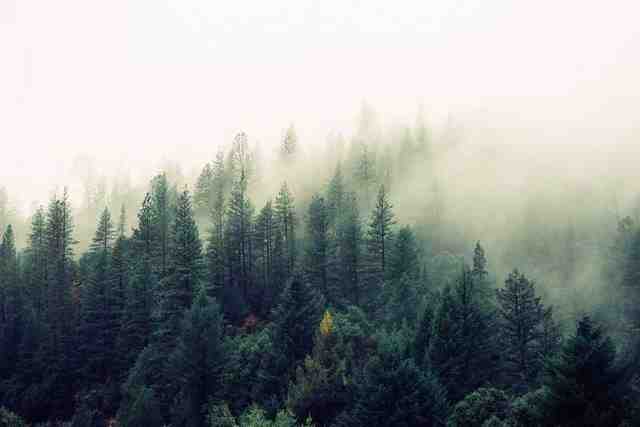

Forest ecosystems mainly consist of trees but also have a variety of plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Further classification of the forest ecosystem is:-
-
Tropical Forest
They receive an abundant amount of rain (100-400 inches) throughout the year.
These forests have dense vegetation and rich biodiversity that accounts for 50 to 80 percent of the world’s plant and animal species.
-
Temperate Forest
They primarily consist of deciduous trees that shed their leaves once a year.
These forests experience a variety of seasons. Temperate forests have low species diversity as compared to tropical.
-
Boreal Forest
Boreal are evergreen forests and also known as taiga.
Most of them are located in arctic regions where the temperature remains below zero.
ii. Grassland Ecosystem
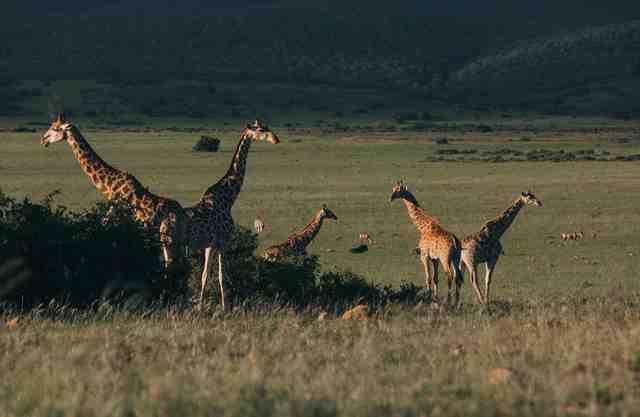

Grasslands ecosystem mainly consists of grasses with a lesser number of trees and shrubs.
They came somewhere between forests & deserts ecosystem and are found in areas where rainfall is not regular.
The two main types of grasslands ecosystem are:
-
Savanna
Savanna is a type of tropical grassland with scattered individual trees.
They exist in warm or hot climates where the annual rainfall is from about 20-50 inches per year.
-
Prairies
Prairies are a type of temperate grasslands where trees and large shrubs are not present.
They mainly consist of different types of grasses and the amount of rainfall is less as compared to savannas.
iii. Mountain Ecosystem
The Mountain ecosystem consists of a diverse range of habitats in which a major portion of plants and animals are present.
They cover almost a quarter of the world’s land area and offer many services such as climate regulation and water provision.
iv. Desert Ecosystem
They have extremely high temperatures with low water availability, thus flora and fauna are rare in the desert ecosystem.
Plants/shrubs like cactus grow in this area that can conserve water as much as possible.
One of the famous desert ecosystems is the Sahara desert.
v. Tundra
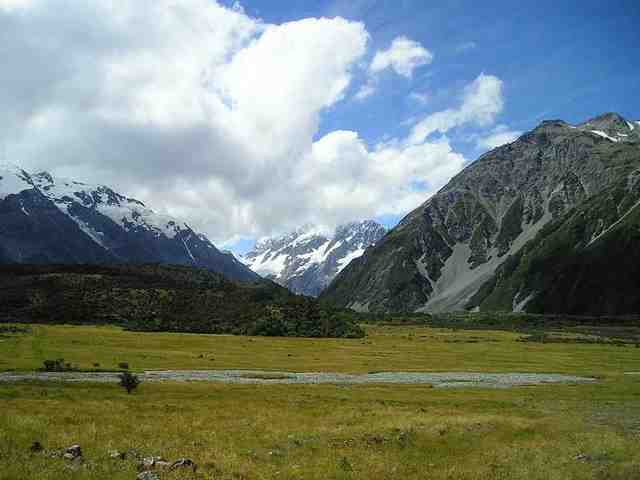

Tundra is a type of ecosystem where low temperatures and short growing seasons hinders vegetation growth.
Some animals living in the tundra region migrate down the mountains during the winter season due to low temperatures.
Tundra is of three types –
- The Arctic
- Antarctic
- Alpine.
What type of Ecosystem do we live in?
We live in a terrestrial ecosystem, as air, a vital component for humanity, is freely available here.
2. Aquatic
|
Aquatic ecosystems also called water bodies are the largest ecosystem on planet earth.
Further classification of aquatic ecosystem is:-
i. Freshwater Ecosystems
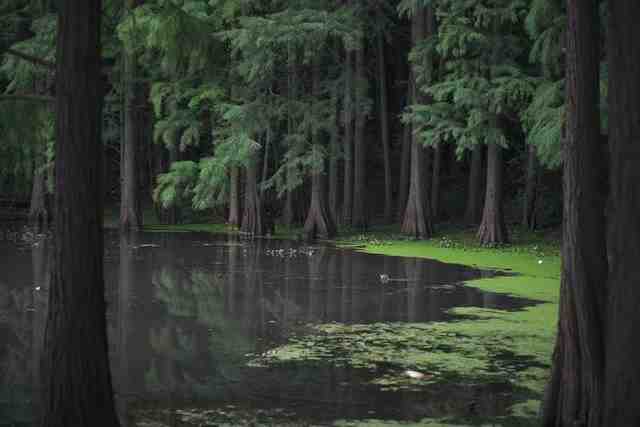

A freshwater ecosystem is widely used as a resource for drinking, agriculture, industry, sanitation, and transportation.
Several freshwater ecosystems consist of a wide variety of organisms, such as fish, amphibians (such as frogs & toads), reptiles, birds, and mammals.
Plants and Phytoplankton (a type of algae that is often consumed by fish) are an important part of the freshwater food chain as they provide oxygen through photosynthesis and food for animals.
While the Earth has 70% water but a tiny fraction, (~2.5%)of it is fresh water and the rest is saline.
Out of this small fraction, only 0.007% is available for consumption.
A freshwater ecosystem can further be broken up into smaller ecosystems :
-
Lakes/Ponds
They are relatively small and often called a slow-moving or still water ecosystem.
-
Rivers
They are fast-moving turbulent water with a high concentration of dissolved oxygen.
It supports better biodiversity than other freshwater ecosystems
-
Wetlands
They are water-saturated soil from a prolonged period.
ii. Marine Ecosystem

They are the largest ecosystems that cover around 70% of Earth’s surface.
Marine ecosystems contain a high amount of dissolved minerals and salts.
It consists of unique biodiversity that supports a wide variety of species.
Apart from various sea creatures, there are thousands of plant species that live in the marine ecosystem.
They depend on the photosynthesis process to get their energy from the sun.
Major plant species are Phytoplankton, seaweeds, seagrasses, and mangroves.
The marine ecosystem mainly consists of the oceans but it can be divided up into three types:
-
Oceans
Atlantic, Arctic, Indian, Pacific, and southern oceans are the major oceans that cover this planet.
They are the most interesting having an enormous range of species and many of them are yet to be discovered.
The oceanic ecosystem is further classified into shallow and deep water surfaces.
-
Estuaries
Estuaries are the water bodies where freshwater from rivers and streams meets with salt-water from the ocean.
Due to their transition from land to sea, this biome contains diverse plant and animal life.
-
Coral reefs
Simply put, Coral reefs are marine organisms made of calcium carbonate skeleton (coral).
Coral reefs act as a buffer to protect the shores from storms and waves.
They also provide food and shelter to the marine inhabitants.
Terrestrial vs Aquatic Ecosystem | What are the differences?
| Terrestrial | Aquatic |
| Land-Based | Water-Based |
| Lower water availability | Ample water availability |
| Great temperature fluctuations | Lesser temperature fluctuations |
| More light availability | Less light availability |
| Oxygen freely available in the air | Oxygen dissolved in water |
| Gravity influenced | Buoyancy influenced |
| Comparatively smaller | Largest ecosystem |
How Energy Flow in Ecosystems?
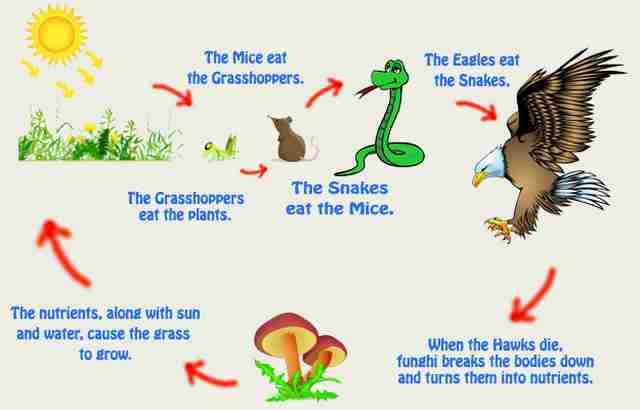
Producers such as plants make their food from sunlight by a process known as photosynthesis and energy is released in this process.
The herbivores feed on plants and then energy is transferred to them.
Their body requires this energy for proper functioning.
Then comes the carnivores that feed on the herbivores and derive energy from them.
Thus we can say that the different plants and animal species are linked to each other through food chains or the food web.
Finally, decomposers like bacteria and fungi break down waste materials and return the nutrients to the soil which can be taken up by the producers.
This chain clearly depicts how energy flow in ecosystems which is well proven by law.
Thus according to the law of conservation of energy –
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can only be transformed from one form to another.
What is the Importance of an Ecosystem?
What do you think about the importance of an ecosystem?
Are they providing any value to human well-being or else they are merely academic stuff?
Let me know your thoughts in the comments.
Let us move ahead.
Now let me ask you something.
Do you enjoy nature and feel much happier when surrounded by it.
If you ask me, I would say I really enjoy it.
We all depend upon nature for our existence and without a healthy eco-system; it is very difficult to survive.
These are the reasons that explain the role and importance of an ecosystem:
1. Maintaining Balance
This is the most important aspect as every living organism relies on ecosystems for its food and habitat.
Just refer to our previous example of lion and deer to see how an ecosystem is maintaining the overall balance.
2. Interdependency
Ecosystems are interdependent and that is why each part of it is essential.
Any imbalance or damage can cause many problems.
3. Life supportive by energy exchange
“Eco-system supports life”, we have to agree with this statement.
We depend upon nature for our survival and without a healthy ecosystem; we would not be getting clean air/water to breathe/drink.
They support life with the exchange of energy and nutrients in the food chain.

4. Resourceful
The eco-system provides all-important natural resources like food, energy, minerals, medicines, water, air, etc.
5. Economically Beneficial
The ecosystem translates the benefits that we receive from nature into economic terms.
How Pollution Affects the Ecosystem?

Pollution is the introduction of harmful contaminants into the air, water, and soil.
Pollution can
- Adversely affect an entire ecosystem
- Cause life more difficult for humans, animals & plants.
- Damage the natural diversity of the eco-system
- Break the food chain
Air Pollution
Air pollutants such as Sulphur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx) ozone (O3), and ammonia (NH3) have major effects on the eco-system and in turn, disturbs the food chain.
For example, Air pollution causes eutrophication and acidification that affects crop yield.
Water Pollution
Water is a necessity for everyone’s life, therefore, its contamination caused by agricultural runoff, mining activities, waste treatment plants, and improperly disposed-of industrial waste is detrimental for our ecosystem.
Land Pollution
The soil fauna regulates the ecosystem through nutrient and carbon cycling that may be at risk by the widespread usage of pesticides.
Heavy pesticide usage can reduce the natural enemies of agricultural pests, which leads to crop yield reductions.
Loss of natural pollinations (bees) occurs due to heavy pesticide usage that can severely impact the ecosystem
Rainwater washes excess chemicals into Lakes, rivers, and seas, polluting both surface water and underground water.
Deforestation also causing huge biodiversity damage due to rising demands for building new cities and transportation systems.
In the end…
In this discussion, we learned about what is meant by an ecosystem, classification, and its importance.
What we need is a good and healthy eco-system that regulates the essential ecological processes, creates stability, and supports life systems.
The eco-system is one of the major entities that control this environment but due to increased pollution, it is becoming fragile on a daily basis.
In order to meet our growing demand for food, water, shelter, and fuel we are harnessing our environment extensively that caused the ecosystem to change over time.
This transformation of our planet has caused substantial economic development and wellbeing at the cost of environmental depletion.
Now the time has come to take care of our ecosystem for the sustainable living of our future generations.
Think & Act!
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecosystem
- https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/ecosystem/
- https://sciencing.com/ecosystems/
- https://s10.lite.msu.edu/res/msu/botonl/b_online/e54/54a.htm
- http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/
- https://www.ducksters.com/science/ecosystems/marine_biome.php