Ethanol as Fuel, is it true?
Yes, the same Ethanol, which is an important ingredient of all alcoholic drinks can be used as a good alternative fuel.
Ethanol, also known as Ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, bioethanol or simply alcohol is made from barley, corn, sugarcane or similar crops by a fermentation process.
In order to reduce toxic gas emissions, the use of ethyl alcohol as an alternative fuel has increased in many parts of the world including India.
Ethanol when successfully blended with petrol (gasoline), increases the octane rating of fuel and due to low carbon emissions, it is less harmful to the environment.
Now you may ask:-
How alcohol is an eco-friendly fuel?
Are there any advantages or disadvantages?
and most importantly, what are the benefits?
Let us discuss each aspect in detail so that you can easily understand and make your valuable contribution to save our environment.
What is Ethanol [Ethyl Alcohol]?
Ethanol is an organic compound with two carbon, 5 hydrogen atoms and a hydroxyl (-OH) group.
The molecular formula is C2-H5-OH (C-Carbon, H-Hydrogen & O-Oxygen) and the structure of ethanol or ethyl alcohol looks like this:-
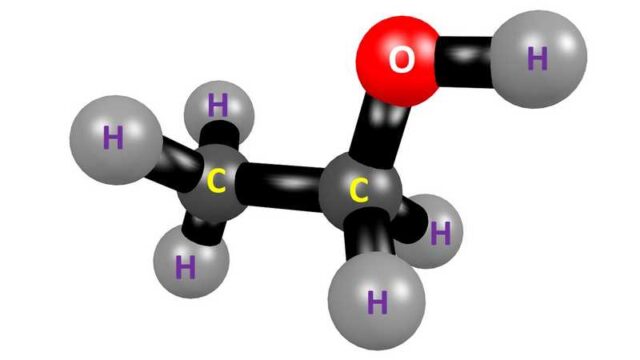
Ethyl alcohol is volatile, colorless and burns with a smokeless blue flame.
Apart from medicinal and recreational (alcoholic drinks) usage, ethyl alcohol is widely used as an alternative fuel when blended with gasoline.
| Gasohol – A mixture of Gasoline (up to 90%) and Ethanol (up to 10%) when used as a fuel. |
What are the sources of Ethyl Alcohol?
The basic raw materials for manufacturing ethyl alcohol are:-
Starch – corn, wheat, barley, and potatoes
Sugar crops – sugar cane, beetroot, and sweet sorghum.
Cellulosic feedstocks – Crop residue or wood chips
In the U.S. and most parts of the world, feedstock for ethyl alcohol production is corn but in India, the feedstock is mainly sugarcane.
Why Ethanol is the best Alternative Fuel?
The most important factor is the Octane rating.
Do you know what an octane rating is?
Octane rating implies the resistance to ‘knocking’, an unwanted sound produced from spark engines during fuel compression.
Higher Octane Rating = Better quality & performance of Gasoline
So you got an idea of octane rating now what it has to do with ethanol?
Ok, I will explain that, but before this, let me tell you something.
Octane Rating of Gasoline Blend: 88 (Regular) – 94 (Premium)
Thus, we found that Ethanol has a higher octane rating than gasoline hence it provides premium blending properties.
Increasing the octane rating for gasoline is expensive and ethanol blending would be a cheaper option.
Practically all modern vehicles can run using a 90/10 gasoline and ethanol mixture while some can use 85/15 mixture too.
Apart from economical benefits, it is harmless for the environment too as ethanol burns more cleanly and completely than gasoline or diesel fuel.
Later, we see more benefits but before that let’s discuss how ethanol can be transformed into fuel.
How Ethanol is Converted into Fuel | Bioethanol Production
Different parts of the world use different types of raw materials for making ethanol as pointed out earlier.
The bioethanol production process remains almost the same whether you use corn or sugarcane.
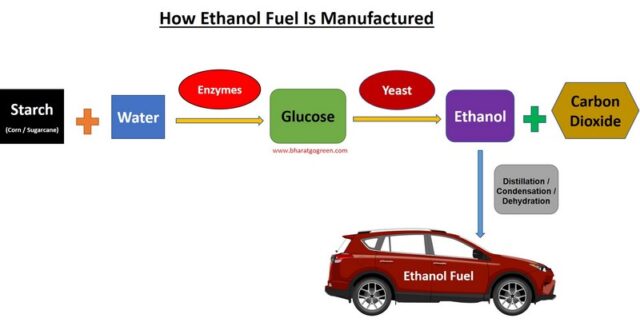
How to make Ethanol using corn?
Ethanol fuel is made by the following process:-
1. Corn kernels are finely ground into the powdery form which is mainly starch.
2. Water is then added to make a slurry.
3. The slurry is heated along with enzyme (alpha-amylase which acts as a catalyst) to break long starch molecules into smaller pieces.
4. The slurry is cooled and a second enzyme (glucoamylase) is added to it. This enzyme converts liquid starch into sugars (glucose).
5. Yeast is added and the slurry is allowed to ferment.
| Fermentation is a biochemical process in which an organism (bacteria or yeast) converts a carbohydrate (starch or sugar) into an alcohol or an acid. |
6. The fermentation process yields only 10-15 % bioethanol that should be concentrated to increase ethanol purity.
7. The product of fermentation is distilled and the evaporated vapor is collected overhead.
8. Overhead ethanol vapors (95 % ethanol) is condensed and cooled into liquid ethanol.
9. The liquid ethanol is then dehydrated to remove excess water.
10. After the dehydration process, pure ethanol is formed which is suitable for blending with gasoline
How to make Ethanol using Sugarcane?
Sugar containing raw materials such as sugarcane, sweet sorghum, and sugar beet are widely used to produce ethyl alcohol.
In India, ethanol is produced from sugarcane molasses due to the wide availability of this crop.
Sugarcane stalks are crushed and squeezed to extract sugar cane juice.
The juice is then transferred to a fermentation tank (containing yeast) where ethanol is produced.
The process is similar to the starch fermentation as described above.
This process is rather old and known as first-generation biofuels.
Now India is ready for Second Generation (2G) biofuels that include raw materials like rice & wheat straw, cane trash, wood, cotton stalk, waste biomass, cellulosic fibers, etc.
Advantages of using Ethanol Fuel
1. Environment Friendly
Ethanol burns more cleaner than gasoline thus creating fewer toxic emissions.
Ethyl alcohol introduces more oxygen into the fuel mixture and improves combustion efficiency.
It does not contain toxic substances like benzene and lead, thus leading to low levels of toxins in the environment.
As ethyl alcohol is obtained from biomass it produces fewer greenhouse gases (GHG) as compared to conventional fuels thus reducing the effect of global warming.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
For developing countries like India, producing & blending ethanol can prove quite cost-effective.
Due to this reason, India’s National Biofuel Policy 2018 specified an ethanol blending target of 10% by 2022 and 20% by 2030.
Any country that produces starch or sugar crops can cut their dependency on conventional fuels as bioethanol is economical to manufacture.
Over the years, significant technological improvements resulted in increased efficiency of corn and ethanol production making it cost-effective.
3. Variety in Feedstock
In addition to corn and sugarcane, a wide variety of crops and feedstocks can be used to make bioethanol.
4. Better Antiknock Properties
Ethyl alcohol has a high octane rating, thus it acts has high-performance fuel with better antiknock properties.
Bioethanol fuel keeps high-compression engines to run more efficiently & smoothly.
5. Reduced dependency on Fossil Fuels
Countries that are not oil producers (such as India) are heavily dependent on the supply of crude oil which is quite unstable.
Bioethanol once produced locally could lead to lower fossil fuel imports.
Adopting ethanol as a fuel can incur huge potential savings for any economy.
Although ethyl alcohol may not replace conventional oil fully in the near term, it can reduce the total amount of oil import.
6. Bioethanol acts as Better Fuel for the Engines
Fuels that are blended with ethanol keep the vehicle’s fuel system clean for optimal performance.
It also helps to prevent winter starting problems by acting as an antifreeze.
7. Creation of domestic Opportunities
Bioethanol production supports local farmers and creates domestic jobs in rural communities.
Bioethanol industry has the potential to create new markets for allied industries such as biomass, agriculture, forestry, construction, food processing, etc.
This is like a chain reaction that helps to strengthen and diversify the rural economies of a country.
8. Easy Accessibility
Locally grown natural raw materials are the feedstock for bioethanol production.
Almost every country grow their foodgrains locally thus, the finished product is readily accessible to all.

Disadvantages of using Ethanol Fuel
1. Loss in Soil Quality
Raw materials such as corn or sugarcane if overgrown (for a prolonged period) then the minerals and other organic supplements are totally lost from the soil.
Thus proper crop rotation is mandatory to improve the soil quality.
2. Not Profitable to Export
Overall, the energy produced by ethanol could be on the neutral side if we include the additional energy required for transportation and processing.
The countries that use ethanol as fuel are producing it in smaller quantities just to meet their domestic fuel demand.
In that way, bioethanol would not be a profitable source of income if it is exported to other countries.
3. Low Fuel Economy
Due to the low energy content in ethanol fuel (about two-thirds that of gasoline), the milage of your vehicle would be less.
Energy Content (Lower heating value) of gasoline is 112,114 -116,090 Btu/gal whereas for ethyl alcohol it is 84,530 Btu/gal.
Thus you can see how ethanol fuel results in lower fuel economy.
4. Feedstock cultivation requires a large piece of land
In order to meet the growing fuel demand, feedstock cultivation requires large scale production.
A large piece of land might not be a problem in some countries but renting and leasing would incur an additional cost.
5. Increased food inflation
let us take the case of India which is one of the largest producers of sugarcane.
If bioethanol demand is more then farmers will concentrate more on ethanol production rather than other essential commodities such as sugar.
Thus, over time, the cost of essential commodities may rise leading to high food inflation.
6. Bioethanol is Corrosive
Ethanol has an ability to absorb water and its corrosive nature makes it difficult to transport through the pipelines over long distances.
water contaminated bioethanol fuel could clog/damage the fuel pipes if a vehicle remains idle for a long period.
Due to its water affinity ethyl alcohol is not suitable for marine environments too.
Conclusion
Ethanol is gaining support nowadays as it is environmentally friendly and causes reduced emissions.
During its implementation, it must be noted that not all vehicles can run on bioethanol fuel especially the older ones.
There are ample benefits of ethanol fuel and on the other hand, there are certain limitations too.
There is always an issue in the supply of feedstocks especially for countries like India where sugarcane cultivation is cyclic.
The second-generation (2G) biofuels technology for ethanol production is still in the nascent stage that needs to be upgraded and refined for commercial usage.
But it is true that even after all these limitations, ethanol-based fuel is still an important alternative as compared to fossil fuels.
Do you have any comments on the article?
Please write to us and don’t forget to share and subscribe.
References:
- https://vikaspedia.in/
- https://www.eia.gov/
- https://web.extension.illinois.edu/
- https://afdc.energy.gov/