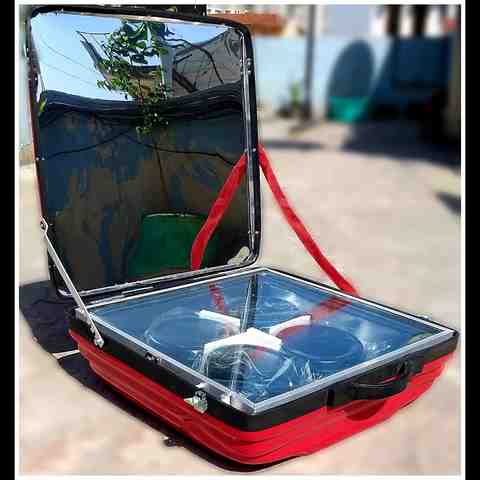
A solar cooker is a primary appliance that utilizes sunlight as an energy source to cook food.
The best part is that no other source of energy is required for a solar stove to operate.
We know that cooking is the most essential and energy-intensive operation in our daily life where a lot of fuel is consumed.
Indian urban regions use electricity and LPG as the primary fuel. However, rural areas still rely on kerosene, dung cakes, and firewood that creates a lot of indoor air pollution.
Apart from environmental pollution, traditional energy sources can cause health & safety hazards such as fire and the generation of unburnt carbon particles.
Solar cooker offers a better cooking solution in a clean and eco-friendly way by using the most trusted renewable energy source – “ The Sun”.
This article will discuss all information about solar cookers, their types, the working principle, their advantages, and disadvantages.
What is a Solar Cooker?

A solar cooker is a device to cook, heat, dry, and bake foodstuffs using direct sunlight instead of gas or electricity.
In developing countries like India, most of the population does not have access to safe drinking water, and solar cookers can be used to sterilize the untreated water.
Gone are the days when a solar cooker was considered merely as a middle school science project that works very slowly?
Due to various technological advancements, new solar cookers take less time in cooking, and they are now competing with the traditional ovens.
A solar cooking device is most suitable for rural India due to:
- Abundant sunlight
- Easy Operations
- No fossil fuel requirements
- Negligible operational and maintenance cost
- Multiple Usage
How Solar Cooker Work? [Basic Working Principle]
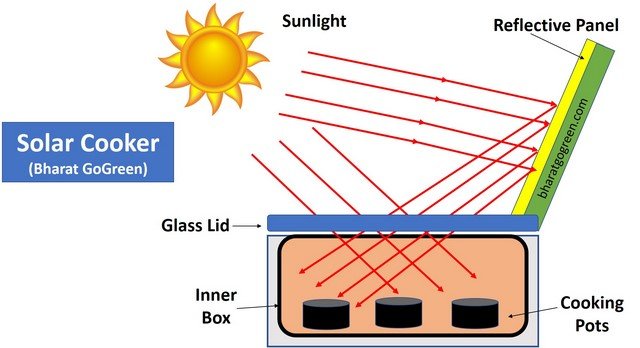
The basic working principle of a solar cooker is to convert sunlight into heat energy and retain it to raise the temperature of the box to a sufficiently high level.
If you think that the direct sun’s heat or ambient temperature is responsible for cooking, then you may be wrong.
Although they can slightly affect the cooking rate, the captured solar radiation is doing the primary job.
When passed through the dark-colored (usually black) interior, these radiations get converted into heat, which is unable to escape the enclosures and achieve a cooking temperature in the range of 65 to 400-degree centigrade.
In all designs of solar cooking equipment, three main working principles are applied to achieve effective cooking;
1. Concentration/Reflection of Sunlight
The concentration of sunlight means focusing it to a specific point to generate maximum heat.
This task is executed effectively by using mirrors and shiny reflective panels that concentrate the sun’s ultraviolet rays to a certain point.
These reflective panels use silver, aluminum, or chromium that multiplies the amount of solar heat received inside the cooking chamber due to maximum reflection.
Do you know what will happen if solar cookers are constructed without reflector panels?
The reflector panel speeds up the heat accumulation process. Without the panels, sun rays alone can take a much longer time to heat the surfaces.
2. Absorption and Heat Generation
The Conversion of light into heat is maximized by using lighter, thinner materials to conduct quick heat transfer.
Dark-colored surfaces absorb heat very well, while light-colored surfaces do not.
The solar cooker interiors and cooking pots are usually black colored to intensify the absorption of solar energy.
The matte black-colored cookware and interiors act as a receiver that converts the incident sunlight into heat by conduction process.
3. Heat Retention
The aim and design of the solar cooking system are to prevent the absorbed incident radiations from escaping through the internals.
Longer heat retention inside the solar cooker leads to maximum cooking efficiency.
Proper insulation and an inverted, transparent glass lid on the top of solar cookers can help achieve maximum cooking efficiency and avoid heat loss.
Sometimes, wrapping a heat-resistant transparent plastic bag across the cooking pots can maximize heat retention.
Just imagine what will happen if solar cooking systems have no insulation and top cover to retain the generated heat?
Yes, you guessed it right!
The absorbed heat is lost into the environment leading to reduced cooking efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar Cooker
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Fuel Cost Saving | Sunlight dependency |
| Safe (No fire or smoke) | Back-up requirement in case of weather changes |
| Retention of nutritious value | Time-consuming (Some Type) |
| Government subsidies | Less efficient |
| Pollution-free | Costly (Some Type) |
| Inexpensive (Some Type) | Sun tracking |
| Multiple types of cooking | Reflective surfaces can damage eyesight |
| Available in Various Size | |
| Some are very easy to construct at home | |
| Silent in Operation | |
| Portable | |
| No Maintenance cost | |
| No dependency on fuel | |
| Easy to Clean |
Uses of Solar Ovens
Solar cooking systems have multiple household usage like;
- Cooking
- Frying
- Roasting
- Baking
- Dehydrate Food
- Water Purification (Boiling)
- Sterilization
- Ironing
What are the types of Solar Cookers?
There are four most common types of solar cookers, and over a hundred variations of the basic types are available in the market.
The cost is widely dependent on the type and size of a solar cooking system.
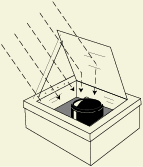
1. Box Type Solar Cookers

For domestic use, box-type solar cookers are the most common having a simple and compact design.
They are cheap and easily constructible by using most common materials but susceptible to wear and tear.
Solar box cookers can attain a temperature of 90 °C to 200 °C, which is sufficient to cook various types of food.
A basic model of box cooker consists of an insulated box with a toughened glass cover painted black from inside to absorb more heat.
A single sheet glass pane is fixed to the box, acting as a reflector for allowing the incident sunlight to fall on the glass cover of the box.
Black absorbing containers made from aluminum are kept inside the box for cooking purposes.
Box-type solar cooker usually takes 1.5 to 2 hours to cook everyday food items such as rice and vegetable.
Box-type solar cookers can work very well in both direct and diffuse solar radiations. Hence, facing the sun is not required every time.
Price of Box-type Solar Cookers
Depending on the size and model, the cost ranges from Rs. 2500 to 6500 for a meal capacity of 4-8 persons
Pros and Cons of Box Type Solar Cooker
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
2. Panel Solar Cooker
The operation of a panel-type solar cooker is quite similar to that of a box-type that uses inside insulation and multiple reflective panels.
They have a larger reflector area to attain a temperature of 150 to 250 °C quickly.
Like box cookers, panel types are also sun-oriented and typically do not require turning to follow the sun during a 2-4 hour cooking period.
When cooking conditions are not that good, then the cooking pot is placed inside a transparent and heat-resistant plastic bag to retain heat.
Cost of Panel type Solar Cookers
Depending on the size and model, the cost ranges from Rs. 5000 (Basic) to 35000 (Advanced) for a meal capacity of 4-8 persons.
Pros & Cons of Panel Type Solar Ovens
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
3. Parabolic Solar Cooker
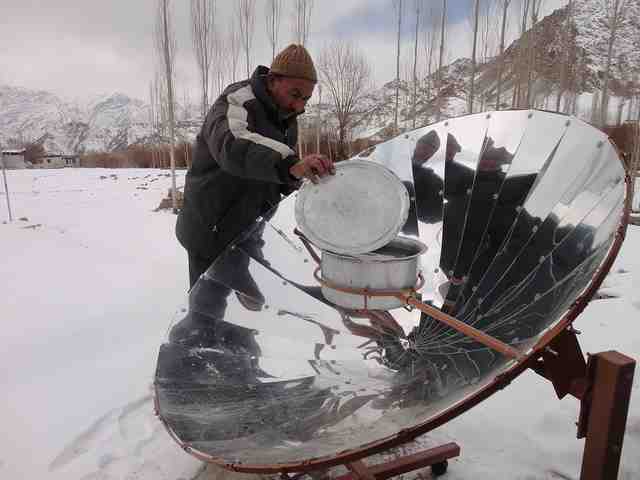

This solar cooker uses a parabolic-type reflecting concentrator that focuses the solar radiation on a fixed area, usually on a cooking pan.
Parabolic solar cooking equipment can quickly reach a temperature of over 200-350 °C (just like a conventional cooking stove) when correctly positioned.
They need frequent repositioning (usually 15 minutes) towards the sun, and many of them have an inbuilt turning mechanism.
This turning or tracking mechanism rotates the solar disc in the sun’s direction to concentrate the solar radiations more accurately.
Price of Parabolic Solar Cookers
The typical cost of a parabolic solar cooker ranges from Rs 7500 to Rs 50, 0000 depending upon the size and the model.
Pros & Cons of Parabolic Solar Ovens
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
4. Vacuum Tube Solar Cookers
They are the most advanced solar cooker available in the market that uses a double wall glass tube as a cooking chamber.
Vacuum is created inside the glass space allowing excellent heat retention capabilities by acting as a perfect insulator.
They use small parabolic reflectors that precisely reflect the sunlight onto the cooking tube.
Vacuum tube solar cookers can easily attain a temperature of 250°C + range, and remain hot for hours, but they have limited capacity.
Price of Vacuum Tube Solar Cookers
Vacuum Tube Solar Cookers’ typical cost ranges from Rs 15000 to Rs 50000 depending upon the size and the model.
Pros & Cons of Vacuum Tube Solar Ovens
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
Solar Cooking in India
In the early ’80s, the Indian government has extensively promoted extensively box-type solar cookers by allowing a subsidy of 30%.
Later in the mid-’90s, after reducing subsidies to 15% and no technological advancements, its sales nosedived.
The parabolic type solar cooker is recently popular between Indian households, large communities, and industrial installations.
Do you know that parabolic-type solar cookers installed at Shirdi Saibaba Temple serve over 25,000 devotees daily and save RS 30 Lakhs/year on fuel and other costs?
Ye, It’s great!!
In 2020, Indian government initiated the development of low-cost indoor solar cooking solutions where Indian Oil (IOC), in partnership with Sun Bucket System (a US-based start-up), will work in the niche area of solar energy-based products.
According to a report by Zion Market Research –
Solar cooker market global demand valuation was approximately USD 1,845.0 Million in 2019 and is expected to generate revenue of around USD 3,209.3 Million by end of 2026, growing at a CAGR of around 8.7% between 2020 and 2026.
In India, solar cooking has the maximum potential for the government-backed mid-day meal program for schools that can be implemented.
Many companies in India also started manufacturing solar cookers aggressively.
The updated list of companies manufacturing various types of solar cookers in India are;
- Rudra Solar Energy, Ahmedabad
- VeSAT Solar Energy Systems, Coimbatore
- Kavita Solar Energy Pvt. Ltd, Ghaziabad
- Jay Renewable Energy Pvt. Ltd, Sangli, Maharashtra
- Enolar Systems, Bangalore
- Sun Technologies, Secunderabad
- NUCIFERA Solar Energy Systems, Karnataka
- Vijaya Industries, Udupi
- Ados Renewable Pvt. Ltd, Dehradun
- Solar World, Rajkot
- Arsh Electronics Ltd, Delhi
If you want to download the whole list of MNRE approved manufacturers then Click here
Conclusion
I hope that the above information about solar cookers helped you understand their basic working principle, uses, types, advantages, and disadvantages.
Indeed solar cooker has many distinct advantages, and they are ideal for camping or other outdoor activities.
New variants of solar cookers are fast enough in cooking, and you can use them even for baking, frying, and grilling various foodstuffs.
Solar cooking systems come in a wide range of prices, but you may opt for box-type solar cookers for a limited budget.
For best performance, vacuum tube and parabolic type solar cookers score better than box and panel type as the former can quickly reach high temperatures in the range of 300+ degree C.
Solar cookers are now complementary to the conventional cooking systems but soon they will replace them as technology advances.
Do you own a solar cooker?
Please provide your comments below and share this article to help others.
To join the Save Environment bandwagon consider subscribing bharatgogreen.
References:
- http://mnre.gov.in
- https://solarcooking.fandom.com/
- http://www.indiasolar.com/SOLCOOKMFR.htm
- Ghodake, Dattatraya. (2016). A Review Paper on Utilization of Solar Energy for Cooking.
- Joshi, Smita. (2017). Solar cooker- A Review.
- wikipedia.com
We are a participant in the Amazon Services (India) Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.in.


