As environmental concern deepens, Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming the latest buzzword in India.
Do you know the reasons why the earlier version of Electric Vehicles was not so popular in India?
Yes, You guessed it right. That was due to the high cost of batteries, longer charging times, and low mileage.
But now times are changing and now EVs are rapidly catching up with conventional fuel vehicles.
Is India ready for electric vehicles now?
In this article or you can say a detailed essay, we will discuss:-
- What is an electric vehicle and how do they work?
- What is the cost of battery replacement in India?
- Advantages and disadvantages of electric vehicles
- What is the future of electric vehicles in India?
After our discussion, you will come to know how EVs can save your money and the environment.
What are Electric Vehicles?
Electric vehicles are solely powered by electricity (partially in the case of Hybrid vehicles) and they are also called Eco-friendly vehicles.
Unlike conventional IC 87engines (diesel or petrol) vehicles, EVs use an electric motor that receives its power from rechargeable batteries or a fuel cell.
Since electric vehicles run on electricity, so there are no harmful exhaust emissions and our environment stays protected from greenhouse gases.
They also have fewer moving parts as compared to the traditional fuel vehicles so there are fewer chances of wear and tear, hence less maintenance cost.

What is the Full Form of EV?
The full of EV is Electric Vehicle
Hybrid Vs Electric Vehicles | What is the difference?
Usually, people use the term Hybrid and Electric interchangeably, but technically, if we see there is a considerable difference between them.
In simple terms,
| Electric Vehicles are totally powered by electricity whereas hybrid vehicles run on Electricity and conventional fuel. |
In India Toyota Camry, Honda accord and many others are available in hybrid variants.
Damerow Ford has given a very nice info-graphic about them, have a look.
Why You Should Prefer EV?
Do you know why electric transport should be your first priority?
Do you think what are the reasons to switch from conventional fuel vehicles to electric ones?
These are some reasons:-
- Technological advancements
- cost-effective & improved batteries production
- An increasing number of charging facilities
- Rapidly depleting fossil fuels
- Volatile geopolitical situations
- Rising energy costs
- Concerns over climate change
How does an Electric Vehicle Work [With Diagram]?
From the outside, any electric car will look like a conventional fuel vehicle but from inside major components such as the IC engine, Catalytic converters, muffler, fuel tank, and the exhaust pipe is not available.
All types of vehicles (petrol, diesel, gas, or electric) can be considered energy conversion devices.
They function by transforming the stored (potential) energy into movement (kinetic energy).
In a conventional fuel vehicle, the energy is stored in a chemical form inside the fuel tank.
Heat energy is released during the internal combustion of the fuel-air mixture which pushes the piston to turn the wheels.
Electric cars also use the stored chemical energy present inside the batteries.
This energy is released in an electrochemical form to move the motor.
Since no combustion is taking place so there are no chances of air pollution or emissions from the tailpipe.
After the release of electrochemical energy, the batteries will be discharged in a similar way as the fuel tank gets emptied.
See the Working principle of an EV (Credit: Learn Engineering Team)
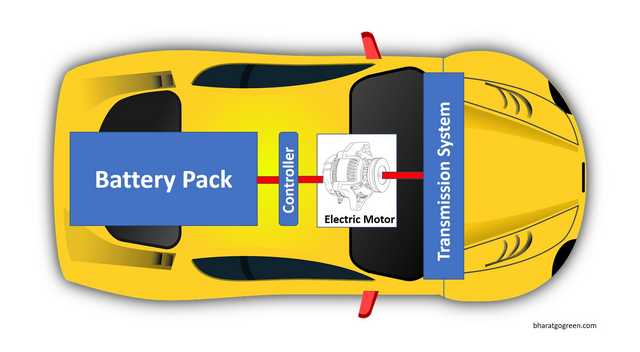
Major Components & Parts of an EV with their Functions:
Let us now discuss about various parts of EV and their functions.
1. Battery Pack
A battery pack inside an electric vehicle consists of a number of cells that are assembled into modules.
These battery modules are installed in the base of the car.

An electric motor uses electrical energy which is stored in batteries.
The stored electrical energy in a battery is denoted by Kilowatt-hours (kW.h).
For example, In India, Tata Tigor EV has a 16.2 kW.h capacity Li-Ion battery and has a range of 142 km whereas the Hyundai Kona has a 39.2 kW.h battery having a range of over 450 Km.
2. Electric motor
The electric motor is the main part of EV that can be AC or DC type but a brush-less DC motor is the preferred choice as it is cheaper.
An electric motor converts the electrical energy (received from the battery) to mechanical energy that moves the vehicle forward.
3. Controller
It is the brain of an electric vehicle that regulates the amount of power received from the batteries and manages the flow of electrical energy.
This part also controls the speed and torque produced by the electric motor.
As the accelerator is pressed the controller will give an output power accordingly.
3. Auxiliary Battery
The auxiliary battery provides electricity to power up the vehicle accessories such as wipers, radio, lights, air conditioners, etc.
4. Transmission System
The electrical vehicle’s transmission system transfers mechanical power from the electric motor to drive the wheels.
5. Charging port
In order to charge the battery pack an external power supply to be connected to the charging port.
6. Converters/Inverters
This part of EV can be DC to DC or DC to AC.
Inverter – An inverter is an electrical device that converts DC power to AC power which can be used for an electric motor.
Converter – DC to DC step down voltage converter converts high voltage DC power from the battery pack to the low voltage DC power which is required to run vehicle accessories.
Apart from the above-mentioned components, some electric cars such as Tesla Roadster use the concept of regenerative braking.
What is Regenerative Braking in Electric Vehicles (EV)?
In fossil fuel-powered cars a lot of kinetic energy is wasted as heat when brakes are applied.
What will happen if there is a kind of braking system that recaptures most of the vehicle’s kinetic energy and convert it into electricity?
| Regenerative braking is a system in which an electric vehicle uses the forward momentum of the motor to recharge the battery. |
In this way, it can recover up to about 15% of used energy.
When we step on the brake pedal of an electric vehicle, the regenerative braking system puts the vehicle’s electric motor into reverse mode, causing it to run backward and slowing down the vehicle.
At the same time, the motor will act as an electric generator and start producing electricity that will be fed into the batteries.
Know Everything about Electric Vehicle Batteries
EV Batteries are the ultimate power source that gets its power from hundreds of batteries joined together as a pack.
Which Type of Battery an Electric Vehicles Use?
Based on the applications, cost, and benefits several battery technologies are in use.
Battery capacity has a direct impact on the vehicle range and as more batteries are added to the vehicle, the size and cost of the vehicle increases.
The most common types of EV batteries are:
1. Lead-Acid Type Battery
Lead-acid batteries have been used in traditional electric vehicles as they are relatively economical.
Now, they are obsolete due to their lower life cycle and poor specific energy (35-40 Wh/kg).
In battery terminology, specific energy determines the battery weight required to achieve a given electric range.
It also indicates how much energy a vehicle consumes.
2. Nickel Metal Hydride (Ni-MH) Battery
Ni-MH batteries are infrequently used in electric vehicles as this technology is also matured by now.
They are superior as compared to lead-acid batteries due to the higher specific energy (60-100 Wh/kg).
Ni-MH batteries have certain limitations such as self-discharging at high temperatures and low charge/discharge efficiency (65%).
3. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Battery
Recent EVs are now using Lithium-ion batteries but they are still the most expensive.
High specific energy (100-260 Wh/kg), low self-discharge rate (5% per month) and more than 85% charge/discharge efficiency make Li-ion batteries most suitable for electric vehicles.
The weight of the vehicle will also be reduced significantly after installing Li-ion batteries.
Overheating & short life span are some of the major limitations of Li-ion batteries.
What to Look in a Battery While Buying an Electric Car?

The EV battery should be based on lithium-ion technology and having a higher capacity as per your requirement.
Battery capacity specifies how much energy the battery contains and it is expressed in kW.h (kilowatt-hours).
Battery Capacity is directly proportional to the vehicle range.
It means that if you have to travel short distances within the city then you may choose a small vehicle with a low or medium capacity battery. This can save you a lot of money.
But do remember, if you have an electric vehicle you must have a 240V line to plug your charger.
Lesser than this would deliver very little power and it will take a long time to charge the batteries.
As an example, Mahindra e-Verito has a 13.91 kW.h lithium-ion battery which can go up to 110 Km while Tata Tigor EV has a 16.2 kW.h capacity Li-Ion battery and has a range of 142 km.
How long does the EV Battery Last?
Indian EV manufacturers provide battery warranties ranging from 3 to 5 years.
For example, Mahindra offers a standard warranty of 3 years/60000 km on the battery of their e20 Plus model.
What is the Cost of Battery Replacement for an Electric Vehicle?
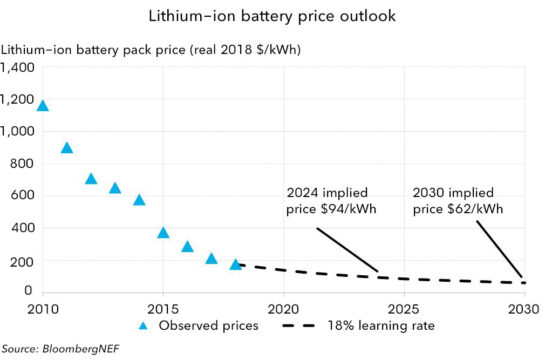
A study was done by Bloomberg (see graphic below) shows the cost of Li-ion battery costs has reduced from $1000/kW.h in 2010 to $200/kW.h in 2018.
They predicted that the price of an average battery pack to be around $94/kW.h by 2024 and $62/kW.h by 2030.
What does it mean?
The cost of battery replacement of an electric car in today’s scenario depends on the type and capacity of the battery-
For example, the Battery replacement cost for Mahindra e20plus, P4 variant battery (capacity – 11 kW.h) would be approx. INR 80,000-1.25 Lakh (including labor cost and considering USD to INR = 74)
But In the future, the cost would come down definitely.
How Long Does It Take to Charge an Electric Vehicle?
The time required to charge an electric car may vary from 1 to 10 hours depending on the type of charger used.
Charging time depends upon the capacity of the battery as well as the power of the charging point.
For example – the Mahindra e20 plus, P2 variant has a 15 kW.h battery that is taking 7 hr 20 min to charge with a 3 kW single Phase 16 Amp Charger while it takes only 1 hr 35 min with 10kW 3 Phase 32 Amp charger.
Similarly, the e20plus P4 variant having a battery capacity of 11 kW.h is taking 6 hrs to charge completely with a 3 kW single Phase 16 Amp Charger.
Advantages of Electric Vehicles in India [Pros]
There are many reasons why you should invest in an electric vehicle now as they have the following advantages:
1. Instant Saving during the Purchase of EV
The Indian government is providing many incentives and tax rebates on the purchase of new electric vehicles.
GST rates on electric vehicles (EV) have been revised to 5 percent from the existing slab of 12 percent.
As per the union budget, anyone taking a loan to purchase an electric vehicle will get more tax benefits.
The Indian government is providing an additional income tax deduction of Rs 1.5 lakh on the interest paid for a loan taken to buy an e-vehicle, with a total exemption benefit of Rs 2.5 lakh over the entire loan period.
2. EV offers Prolonged Saving Due to Low Maintenance Cost
Electric cars run on electric-powered engines having a lesser number of moving parts and require no lubrication.
Due to the absence of multiple moving parts they have less wear and tear as compared to conventional fuel vehicles.
Thus, you can save a lot on maintenance costs as green vehicles need not be sent to service stations too often.
3. Saving on Fuel Cost
With rising fuel prices, driving conventional vehicles can burn a hole in our pockets.
Although, electricity is not free in India running an electric vehicle is far cheaper and convenient.
Mahindra e-Verito claims a running cost of Rs 1.15 per km (18 units of electricity consumed at 7 Rs a unit, at a range of 110 km.)
If we consider conventional petrol cars, then they have a running cost of about Rs 5.5 per km (Cost of petrol Rs 100/lit and average mileage of 18 Km/l is considered)
4. Saving on Public Transportation Cost
In India, there are a majority of people relying on public transportation only.
The Indian government is promoting the electrification of public and shared transport in the second phase of the FAME India 2 program.
Within the next three years, the Indian government will purchase 500,000 electric tricycles and 7,000 electric buses for public transportation.
Hence public transportation costs will be coming down in the future.
5. Environmental Protection
Green transport does not generate any toxic tailpipe emissions which can be considered a major source of air pollution in India.
Electric motors are much smoother and quieter than conventional IC engines hence they limit noise pollution too.
6. Electric Vehicles are becoming Safer and Secure
Do you know that EVs undergo the same fitness test as other conventional vehicles?
Nowadays EVs are coming with ample safety & security features such as airbags, Rear Camera, ABS, digital immobilizer, child lock, and many more.
If you have an electric vehicle then you need not go to the refueling stations (Petrol/Diesel). Hence you are safe from cancer-causing (carcinogenic) toxic emissions that are present at petrol pumps.
7. Electric Vehicles are Energy Efficient
Energy efficiency is the percentage of energy (produced from fuel or electricity) that will be converted into useful work.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy website –
“EVs convert about 59%–62% of the electrical energy from the grid to power at the wheels. Conventional gasoline vehicles only convert about 17%–21% of the energy stored in gasoline to power at the wheels”.
Thus you can see how efficient electric vehicles could be.
You can rely on battery power to travel more kilometers as compared to conventional fuel vehicle tanks.
8. Electric Vehicles have High Performance
Electric car motors are responsive with instantaneous torque and quiet acceleration leading to high performance.
Disadvantages of Electric Vehicles in India [Cons]
Electric vehicles have potential downsides that need to be considered before making a purchase.
1. Electric Vehicles are more Expensive than Fuel-Powered Vehicles
At present, this point stays valid even though the cost of EVs are falling drastically over the years.
However, various tax incentives and fuel cost savings may help you to balance this cost overall.
2. EV Battery Replacement is Costly
Batteries of electric vehicles are required to be changed every 3 -8 years depending upon the type and usage, which could be quite expensive.
3. Limited Range of Electric Vehicles
The majority of electric vehicles in India have a limited range (150-250 Km) on a single charge.
If you like long journeys then the battery needs to be recharged.
But, over time the driving range has been improved and still improving.
For Example, Hyundai Kona has a 64 kW.h battery having a range of over 450 Km.
4. Non Availability of Charging Stations at all locations
In India, electric refueling or charging stations are still in the development stage.
If you are planning for a long trip then re-think before you go.
5. Longer Recharge Time
The time required to charge an electric car may vary from 1-10 hours which depends on the capacity of the battery and the power of the charging point.
Also due to the limited number of charging stations in India recharge time would be more.
6. Lack of Choice
In India, a limited number of electric cars by selected manufacturers are available at present but these numbers will increase over time.
What is the Future of Electric Vehicles In India?
The Indian government is promoting electric vehicles by providing various incentives & tax benefits so the future looks promising.
With the launch of the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020 by the Indian Government, the electric vehicle industry will definitely get a boost.
In order to promote the manufacturing of electric and hybrid vehicles in India, reduce pollution, and cut the costly oil imports, the FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric) scheme was launched in 2015 which has been superseded by FAME II introduced in 2019.
Indian Government is providing income tax benefits up to INR 1.5 lakh on interest paid on loans to buy electric vehicles.
Govt. of India is also giving custom duty exemption on lithium-ion batteries and this will help to lower the cost as they are not produced locally.
Conclusion…
As the demand and price for oil are going upwards, electric vehicles will be the most favored and normal mode of transportation in the coming future.
By using an electric vehicle you are not only saving a handsome amount of money for yourself but protecting your environment also.
The decision of purchasing an electric vehicle solely depends on your personal needs and vehicle usage.
Some Indian companies such as Mahindra and Tata are offering a handful of electric vehicles with outstanding benefits to choose from.
We certainly hope that the choice of electric vehicles will increase in the coming future.
Please let us know in the comments, what do you think about electric vehicles and do you have any plans to purchase them in the future?
Do share this article and subscribe to bharatgogreen.
References:
- https://www.explainthatstuff.com
- http://www.electricvehiclesmalta.eu
- https://afdc.energy.gov
- https://circuitdigest.com
- http://vikaspedia.in
- https://auto.ndtv.com
- https://batteryuniversity.com/