e Waste also known as electronic waste is the world’s fastest-growing waste streams.
They had already crossed an estimated average of 50 million tons in 2018.
Over time, the electronics industry had seen tremendous growth due to immense innovation and falling prices.
Lower end of life (EOL) and charm for faster up-gradation of electronics products compelled the consumers to discard their old products.
This in turn is responsible for the accumulation of huge e-waste.
If we talk about India then according to a report by Global E-Waste Monitor 2017, India generates about 2 million tons (MT) of e-waste annually.
Growing amount of electronic waste, disposal through open burning, improper and unsafe treatment pose a significant hazard to the environment and human health.
Let us discuss the cause, effect and management of electronic waste in more detail.
What is e Waste?
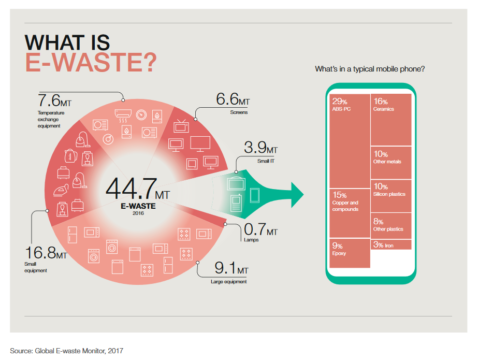
E waste is the outdated / discarded electrical or electronic equipment and its components without any intent of reuse.
It includes a wide variety of products ranging from any household item with circuitry (such as refrigerator, television, air conditioners, mobile, computers, etc.) and electrical/electronic components with power or battery supply.
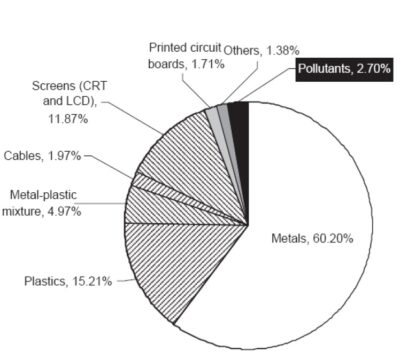
The three main constituents of e-waste are glass, plastics, and metals.
Electronic wastes are environmentally hazardous on one hand and valuable on the other as they contain a substantial amount of precious and rare metals such as copper, gold, silver, nickel, indium and palladium.
It is possible to recover and reuse these metals as raw material for new products.
However, any electronic product can be made of more than 1000 different substances so it is very difficult to do that.
Factors Contributing to e Waste Generation
1. Global information sharing on the rise
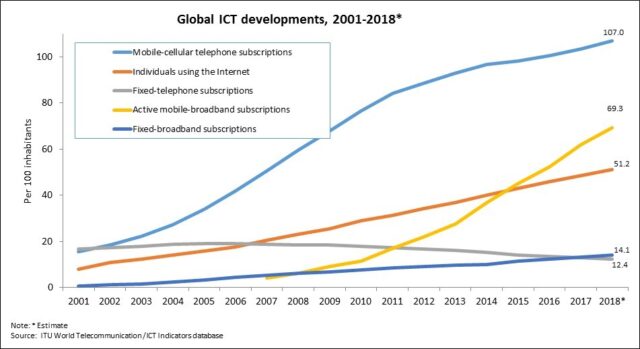
Faster network, application & services requirement amplified in major sectors such as education, health, commercial, entertainment and government.
Rapid expansion in cellular and broadband networks allowed more and more people, especially in rural areas, to have access to the internet and smartphone.
Expanding online businesses and digital marketing has paved a way for increased consumption of IT equipment.
2. Rapid Industrialization and Urbanization in Developing Nations
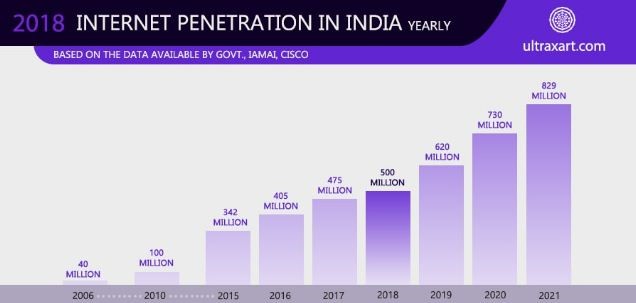
Over time, emerging economies (such as India) with a low purchasing power witnessed the fastest annual growth in electrical and electronic equipment consumption.
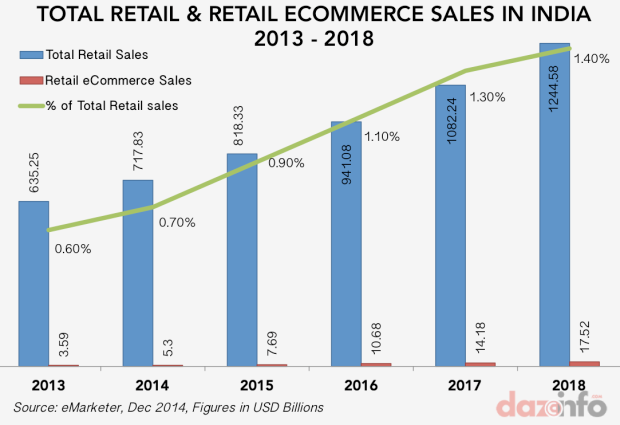
Just refer to the graph below, which clearly shows the increasing trend of e-commerce sales in India.
Higher disposable income led to higher living standards necessitates the consumption of electronic products.
Refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioning, LED TVs and smartphones are the largest consumable electronic items in India.
3. Digital Products and Services are Becoming Cheaper
Fierce competition in telecom markets, technological advancement in mobile computing and falling prices of digital services such as the internet are fueling the widespread usage of electronic products.
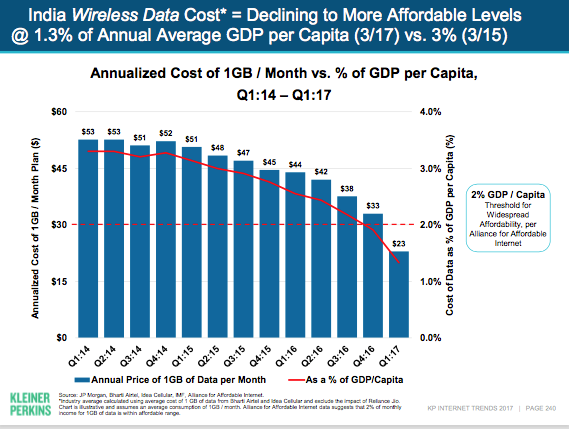
In India, the cost of IT equipment and smartphones are falling rapidly due to continual efforts made through “Make in India” initiative.
As a result, a lot of manufacturers set their plants locally and offer increasingly affordable entry-level smartphones and computers for low-income users.
This means that more people can now afford to buy new equipment, and eventually, more of them will be discarded.
4. Multiple Device Ownership to Build a Digital Ecosystem
What does it mean?
It means that more people want to be connected 24 x7 so they own multiple devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, e-readers, gaming devices, smart televisions, etc.
In order to keep pace with the latest technologies and upgrades, consumers are regularly replacing not only smartphones but also their laptops, routers, TVs and other digital devices.

Digital advertising is also responsible for declaring equipment outdated even if it is not obsolete.
A new growing trend is to throw away and purchase something new rather than keep, repair and reuse it.
5. Conversion of Analog to Digital System
Over the last few years, many electrical/electronic systems are converted from analog to digital.
Some good examples are the television sets, set-top boxes and video recorders.
Many consumers decided to upgrade their analog televisions/CRT monitors for a new digital TV and this switchover created a lot of e-waste.
6. Rise of Cloud Computing and Digital Data Centers
Today, almost all private and government organizations are keeping their mission-critical workloads and data into the cloud servers.
Through the cloud, general consumers can access the digital content and services on multiple devices, almost from any location
Although cloud computing can lead to a reduced number of devices as all services can be accessed from one device but more cloud computing means more data centers and more e waste.
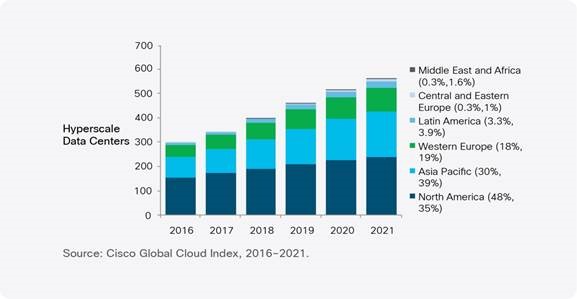
The number of data centers is increasing day by day due to rising traffic, particularly from cloud services. This will continue to grow in the coming years, as per the Cisco Global Cloud Index.
India is undergoing a digital transformation at a rapid pace and in the last few years, it has taken a substantial leap in digital adoption.
Health and Environmental Impact of e Waste
It is hard to believe that around 4000 tons per hour of electronic waste are being generated worldwide.
E-waste contains several components, many of which are inherently hazardous and highly toxic in nature.
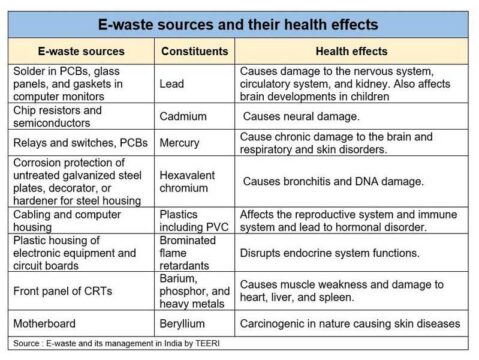
Due to the complex composition, electronic waste handling is a challenge.
Rudimentary disposal and recycling can lead to an adverse impact on health and the environment as well.
In developing countries such as India, e waste recycling is now becoming a source of income.
This is so because the electronic components contain valuable metals such as copper, silver, gold, platinum, etc.
However, in addition to small quantities of valuable components, electronic waste also contain toxic chemicals such as mercury, lead, cadmium, PVC, PCB, arsenic, chromium, selenium, zinc, etc.
Burning/dismantling of these electronic components produces dangerous fumes that are very hazardous to human health.
In India, people working in unorganized sectors (waste pickers) are mostly engaged in collecting, dismantling and recycling e-Waste.
They live in close proximity to dumps or landfills of untreated electronic waste and work without any protection or safeguards.
As per data, informal sectors are responsible for recycling more than 95 percent of e waste in India.
Electronic wastes are hazardous to human health and environment causing air/water/land pollution and adversely affecting food supply chains if not handled properly.
E wastes containing an ample amount of lead materials can damage the human nervous system, kidneys and bones.
Some e-waste is carcinogenic in nature that is very hazardous if not disposed of properly.
e Waste Management | How to Manage Electronic Waste Effectively?
Many developed countries such as the US, Europe, and Japan are using fully automated technologies for e waste recycling.
Electronic waste is crushed, shredded; finally, metals and non-metals are separated by using various unit operations.
A report by the Basel Action Network (BAN), an organization working for the prevention of globalization of toxic chemicals states that US exports approx. 50 to 80 percent of collected e-waste to India, China, Pakistan, Taiwan and a number of African countries.
This is so because cheap labor is available in these countries for e waste recycling.
One side, India is importing a huge quantity of electronic waste and on the other side generating e waste at an alarming rate.
Today, India is one of the largest consumers of mobile phones but most users are still unaware of how to dispose of their e-waste.
Most Indians are selling their e waste to the informal sector that aggravates the health and environmental issues.
You can see the below graph showing city-wise e waste generated in India.
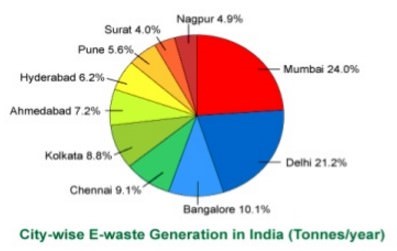
Methods of e Waste Management
Till date, e-waste can be treated by 04 basic ways but none has been found fully satisfactory.
These are:-
♦ Storing in landfills is the most common way but it creates land pollution.
♦ Incineration release heavy metals such as lead, cadmium and mercury into the atmosphere creating air pollution.
♦ Reuse as a refurbished or second hand is a good option but ultimately it will come as e-waste.
♦ Recycling appears to be safest but the process involves dismantling, shredding, burning, etc. that are mostly unregulated and often create additional hazards in itself.
Considering the four alternatives, recycling may be an important solution, especially if we consider that e-waste contains many valuable and rare materials.
Concerns in managing electronic waste in India
♦ E-waste disposal awareness is very low among manufacturers and consumers.
♦ Specific legislation on e-waste management is not available.
♦ No means to collect the accurate data of electronic waste that are being imported, generated and recycled.
♦ The unorganized sector is mainly responsible for e-waste collection and processing using obsolete techniques causing health and environmental problems.
♦ E waste recycling processes are inefficient causing considerable loss of valuable materials.
♦ Inadequate funds.
What Government of India is doing to tackle e waste problem?
In 2011, Indian government passed the first law on e-waste management.
It states that the producer is responsible for the management of final stages of the life of its product in an environmental friendly manner.
Electronic waste collection target was missed in the earlier version so a new set of E-waste (Management) Rules, 2016, came into existence after October 2017.
The present rule states that:-
♦ The Producer is responsible to ensure the take-back of the end-of-life products, which is the global best practice.
♦ Any electronic equipment or spares should not contain pollutants such as lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers beyond a maximum concentration value.
♦ Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) to conduct random sampling of electrical and electronic equipment placed on the market.
Some other initiatives taken by the Indian Government are:-
♦ In order to create awareness among the public about the hazards of e-waste recycling by the unorganized sector, The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has initiated an E-waste Awareness program under Digital India initiatives.
♦ The public is encouraged to participate in ‘Swachh Digital Bharat’, by giving their e-waste to authorized recyclers only.
♦ A dedicated website, Twitter handle and Facebook page is created in order to spread awareness through social media.
♦ The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has developed inexpensive technologies to recycle valuable materials, PCB and plastics in an eco-friendly manner.
This process is cost-effective and suitable for a developing country like India.
Top 10 things we can do to tackle e Waste problem
It is evident that the problem of electronic waste generation should be tackled at a higher level but here are a few things that we can do at our level to minimize e waste.
1. Get Educated
Get awareness about environment protection through blogs and websites.
You can also attend various programs organized by the Indian government from time to time.
Educate everyone so that effective e-waste disposal becomes a practice.
2. Do not Discard just Donate
Many educational institutions can reuse your old electronic gadgets for educational purposes.
You can donate to them or anyone in need.
In India, you may donate your old gadgets through an online platform Budli.
After donation, you will also receive an email electronic donation certificate and tax receipt.
3. Use Replacement Programs
Some electronic companies offer take-back programs for old gadgets.
Amazon, Flipkart and other e-commerce websites have certain replacement offer that can provide some monetary benefits too.
4. Recycle your Old Gadgets

Many big brands like Apple, Samsung, and others started an option to recycle your old electronics.
Sometimes, you may even get financial benefits for recycling your old gadgets.
In India, Samsung has launched an initiative known as Samsung take back and recycling program (STAR) for eco-friendly recycling of e-waste.
You can directly call the company (1800-40-7267864) or mail them to pick-up your old gadgets.
You will also receive a recycling certificate within 30 days from the date of product pick-up
5. Reuse or Repurpose
We can reuse our Old electronic gadgets in many other forms.
For example, Use your Old camera phones as a security camera or your old MP3 player as a USB drive.
You can find many ways to reuse them on the internet.
6. Increase the life span of Gadgets by proper maintenance
In order to save your money and reduce electronic waste keep your electronics well maintained to increase their life span.
You may find thousands of articles and videos over the internet on ‘how to properly maintain your gadgets like smartphones, computers, etc.
7. Expert Disposal
Find out who’s the local e-waste disposal company that ethically disposes of e-waste or refurbishes e-waste and sign up for their services.
You can search on the internet for the same.
8. Reassess your requirements
Want to buy a new mobile phone in a consecutive year…Please think twice.
Just ask a few questions to yourself like –
Does this new gadget is adding any value to my personal or professional life?
Do I really need this gadget?
If your answer is no then you must reassess your requirements.
9. Consider Renting
This will be most relevant to photographers, especially for those who are doing wedding photography.
There are many companies which offer lenses, camera, lighting equipment, props etc on rent so there is no need to buy costly equipment.
Anyway, after some years they are going to be obsolete and discarded.
Most persons are renting the apartments and one can opt for fully furnished apartments if their budget permits.
It may be a bit costly but you can minimize the need for electronic gadgets such as television, AC, refrigerator, etc.
10. Use Cloud Services to reduce e waste

We spend a lot of money on storage devices such as hard disk, USB drive, memory cards, etc. in order to store our data.
These devices are responsible for huge electronic waste creation that no one is anticipating.
Cloud storage can reduce the amount of e waste.
It helps to access our data from anywhere around the world.
Cloud storage is free (at a certain limit) and there is no need to carry your storage device all the time.
You can find here some of the best free cloud services.
Conclusion
Growing streams of e waste is a prime concern for developed as well as developing nations such as India.
Ease of life, higher disposable income and digital penetration led to the usage of more and more electronic gadgets.
Improper disposal and recycling of electronic waste can cause an adverse impact on health and environment which needs to be addressed.
There is immense potential in e waste recycling if done properly and scientifically.
There are few positive movements in this direction, but a lot to be done.
There is a need to overhaul this informal e-waste sector through awareness campaigns, skill development, proper safety measures, specific legislation, adequate funds and introduction of cutting edge technologies.
There are many things that we can do at a personal level to save our environment and reduce electronic waste.
Please tell us what you are doing to reduce electronic waste?
References:
- Recycling of e-waste in India and its potential
- https://meity.gov.in/writereaddata/files/EWaste_Sep11_892011.pdf
- What is e-waste?
- The Problem with E-Waste
- Electronics Recycling and E-Waste
- http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_A_New_Circular_Vision_for_Electronics.pdf
- https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-D/Climate-Change/Documents/GEM%202017/Global-E-waste%20Monitor%202017%20.pdf
- Electronic waste – an emerging threat to the environment of urban India
- Cisco Global Cloud Index: Forecast and Methodology, 2016–2021 White Paper
- https://rajyasabha.nic.in/rsnew/publication_electronic/E-Waste_in_india.pdf
- The A-Z of e-waste management
- A Review of Technology of Metal Recovery from Electronic Waste | IntechOpen